Zambia Flag Meaning
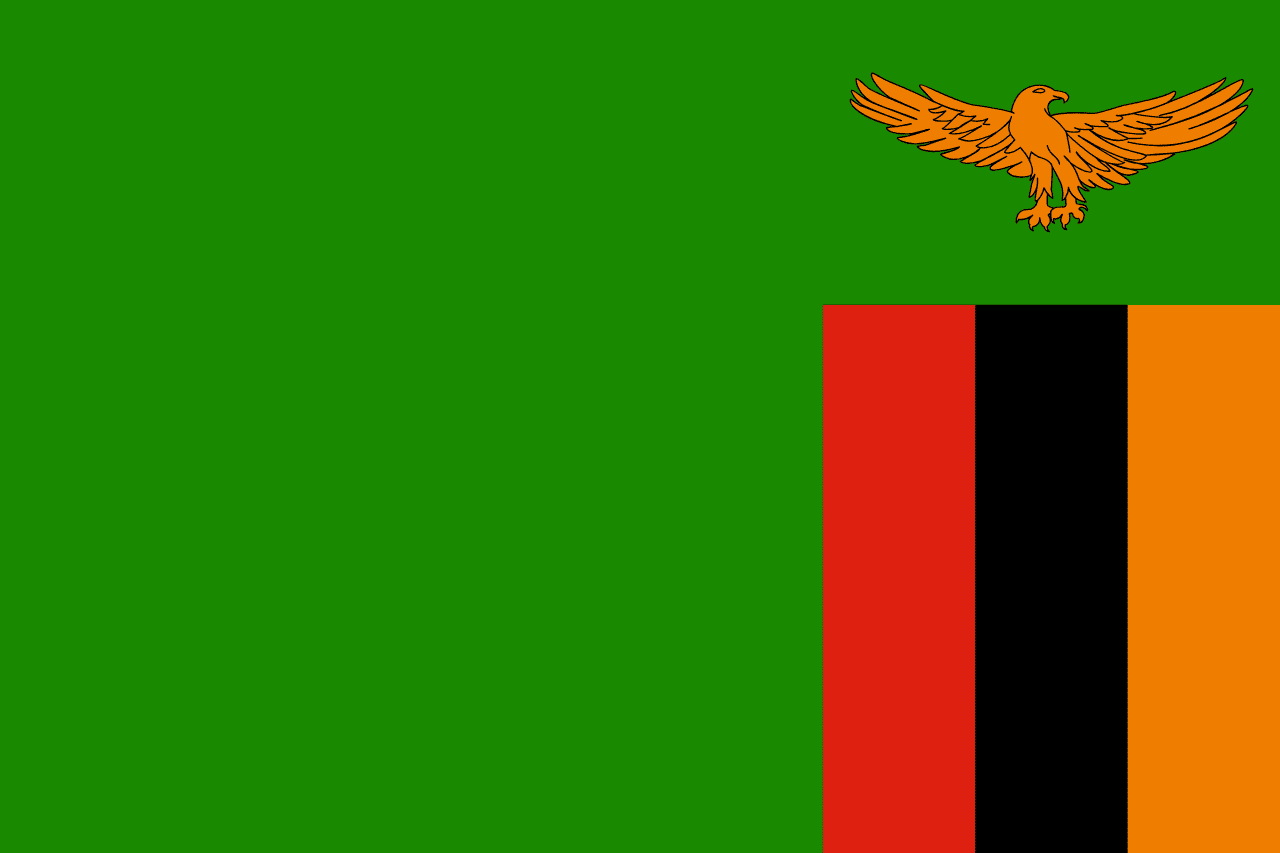
A green field with three vertical stripes of red, black, and orange in the lower right corner and an orange eagle above the stripes, representing the country's natural wealth, the struggle for freedom, the African heritage, the mineral wealth (particularly copper), and the ability to rise above problems.
- Continent
- Africa
- Adopted
- 1964
- Ratio
- 2:3
- Colors
- green, red, black, orange
- Designer
- Gabriel Ellison
Symbolism
Green Field: Represents the lush vegetation, forests, and agricultural potential of Zambia, symbolizing the fertile lands and natural wealth that sustain the nation and provide hope for prosperity.
Red Stripe: Represents the blood shed during the struggle for independence from British colonial rule, symbolizing the sacrifices made by freedom fighters and the courage of those who fought for liberation.
Black Stripe: Represents the African heritage and identity of the Zambian people, symbolizing the connection to the broader African continent and pride in African culture and traditions.
Orange Stripe: Represents the mineral wealth of Zambia, particularly copper which has been the backbone of the economy, symbolizing the underground riches that have shaped the nation's development.
Orange Eagle: Represents the ability of the people to rise above the country's problems and challenges, symbolizing strength, pride, and the aspiration to soar to greater heights as a nation.
History
- Pre-Colonial Era: Various Bantu-speaking peoples established kingdoms and trading networks, with groups like the Bemba, Lozi, and Tonga developing sophisticated political systems and participating in long-distance trade.
- 1855: David Livingstone became the first European to see Victoria Falls, which he named after Queen Victoria, beginning sustained European contact with the region.
- 1889-1924: The British South Africa Company administered the territory as North-Western and North-Eastern Rhodesia, exploiting mineral resources and establishing colonial rule over indigenous peoples.
- 1924-1953: Northern Rhodesia became a British protectorate with direct colonial administration, developing copper mining that would become central to the territory's economy and identity.
- 1953-1963: Northern Rhodesia was part of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, but African opposition to white minority rule led to the federation's dissolution and moves toward independence.
- 1960-1964: Kenneth Kaunda's United National Independence Party (UNIP) led the independence movement, winning elections and negotiating with Britain for self-government and eventual independence.
- October 24, 1964: Zambia gained independence from Britain with Kenneth Kaunda as the first president, adopting the current flag design and establishing a one-party socialist state.
- 1964-1991: Kaunda's rule emphasized African socialism and non-alignment, but economic problems, copper price declines, and political pressure led to growing demands for multi-party democracy.
- 1991: Frederick Chiluba's Movement for Multi-party Democracy (MMD) defeated UNIP in elections, ending 27 years of one-party rule and beginning democratic transition.
- 1991-2011: Democratic governance was established under MMD rule, with economic liberalization and privatization programs, though corruption and poverty remained significant challenges.
- 2011-2021: The Patriotic Front under Michael Sata and later Edgar Lungu governed through a period of Chinese investment and infrastructure development, but also increased debt and authoritarianism.
- 2021-Present: Hakainde Hichilema's United Party for National Development won elections promising economic reform and good governance, facing challenges with debt restructuring and development.
Trivia
- Zambia is a landlocked country in southern Africa, bordered by eight nations, making regional cooperation and trade relationships crucial for economic development.
- The flag represents Africa's largest copper producer and one of the world's major copper exporters, with the Copperbelt region being central to the national economy for over a century.
- Victoria Falls, shared with Zimbabwe, is one of Zambia's most famous tourist attractions and generates significant hydroelectric power for both countries through the Kariba Dam.
- English is the official language of instruction and government, while over 70 indigenous languages are spoken, with Bemba, Nyanja, Tonga, and Lozi being the most widely used.
- Zambia has maintained relative political stability compared to many African countries, with peaceful transfers of power and a functioning multi-party democracy since 1991.
- The country is home to South Luangwa National Park, one of Africa's premier wildlife destinations known for walking safaris and high concentrations of leopards and other big game.
- Traditional ceremonies like the Kuomboka of the Lozi people, where the king moves to higher ground during floods, attract tourists and preserve important cultural heritage.
- The flag flies over a country where about 85% of the population practices Christianity, with various denominations coexisting peacefully alongside traditional African religions.
- Zambian cuisine features nshima (maize meal staple) served with various relishes including vegetables, meat, and fish, reflecting both local traditions and regional influences.
- The country has significant hydroelectric potential due to the Zambezi River system, though development has been limited by financing and technical challenges.
- Zambia's economy has struggled with over-dependence on copper exports, making it vulnerable to global commodity price fluctuations and emphasizing the need for diversification.
- Traditional music includes the kalimba (thumb piano) and various drums, while modern Zambian music blends traditional rhythms with contemporary styles like Zamrock.
- The flag represents a country with a young population where over 60% are under 25 years old, creating both opportunities and challenges for education and employment.
- Zambia has faced significant challenges with HIV/AIDS, though prevention and treatment programs have helped reduce infection rates and improve health outcomes.
- Despite being landlocked, Zambia has developed important regional relationships and serves as a transit route for neighboring countries' trade with international markets.
Related Countries

Zimbabwe
Africa
Seven horizontal stripes alternating green, yellow, red, black, red, yellow, green with a white triangle at the hoist containing a red five-pointed star and the Zimbabwe Bird, representing the nation's agricultural wealth, mineral resources, blood shed for independence, the African people, peace, and the ancient civilization of Great Zimbabwe.
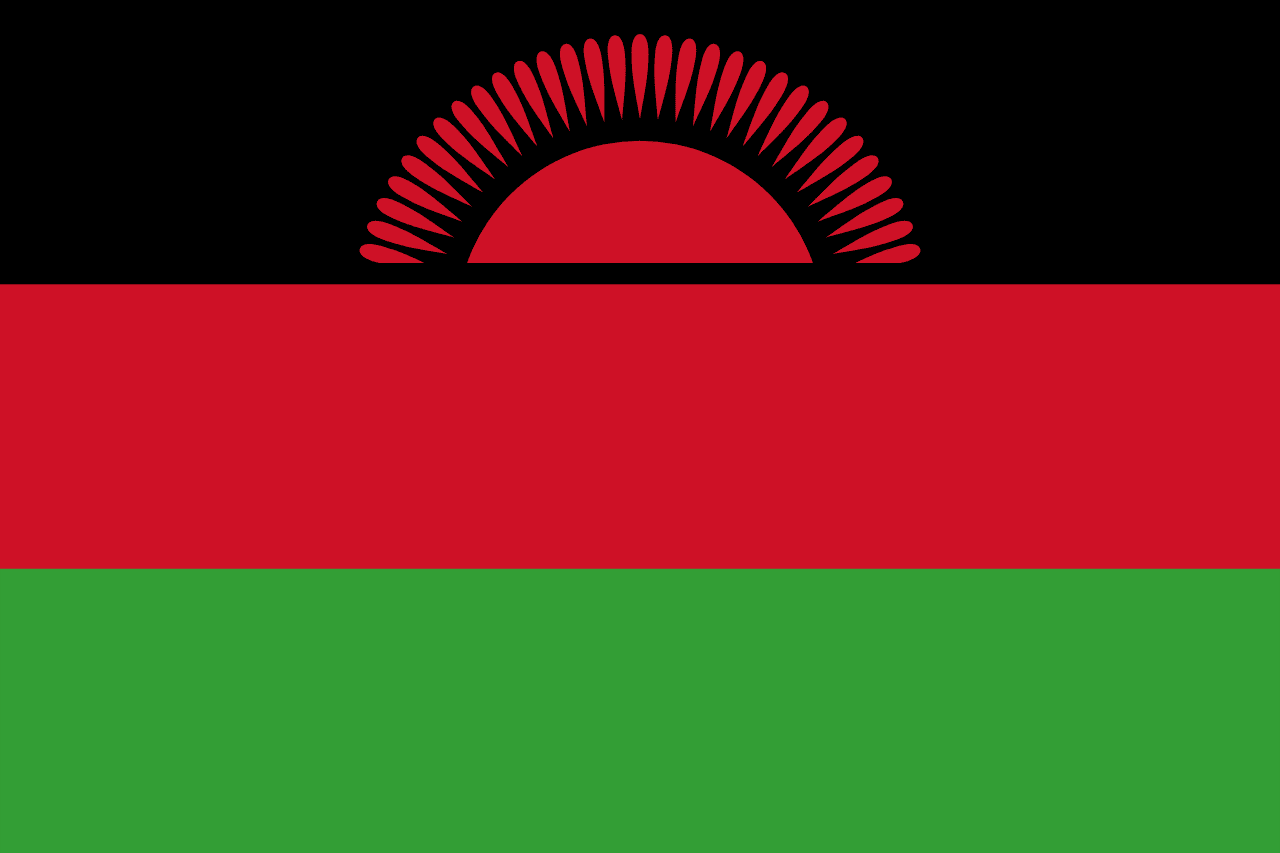

Malawi
Africa
Three horizontal stripes of black, red, and green with a red rising sun in the upper left corner, representing the African people, the blood of freedom fighters, the land's fertility, and the dawn of freedom and hope.

Mozambique
Africa
A horizontal tricolor of green, black, and yellow, separated by white fimbriations, with a red triangle at the hoist bearing a yellow star, a book, a hoe, and an AK-47 with bayonet. The flag uniquely features a modern weapon as a national symbol.
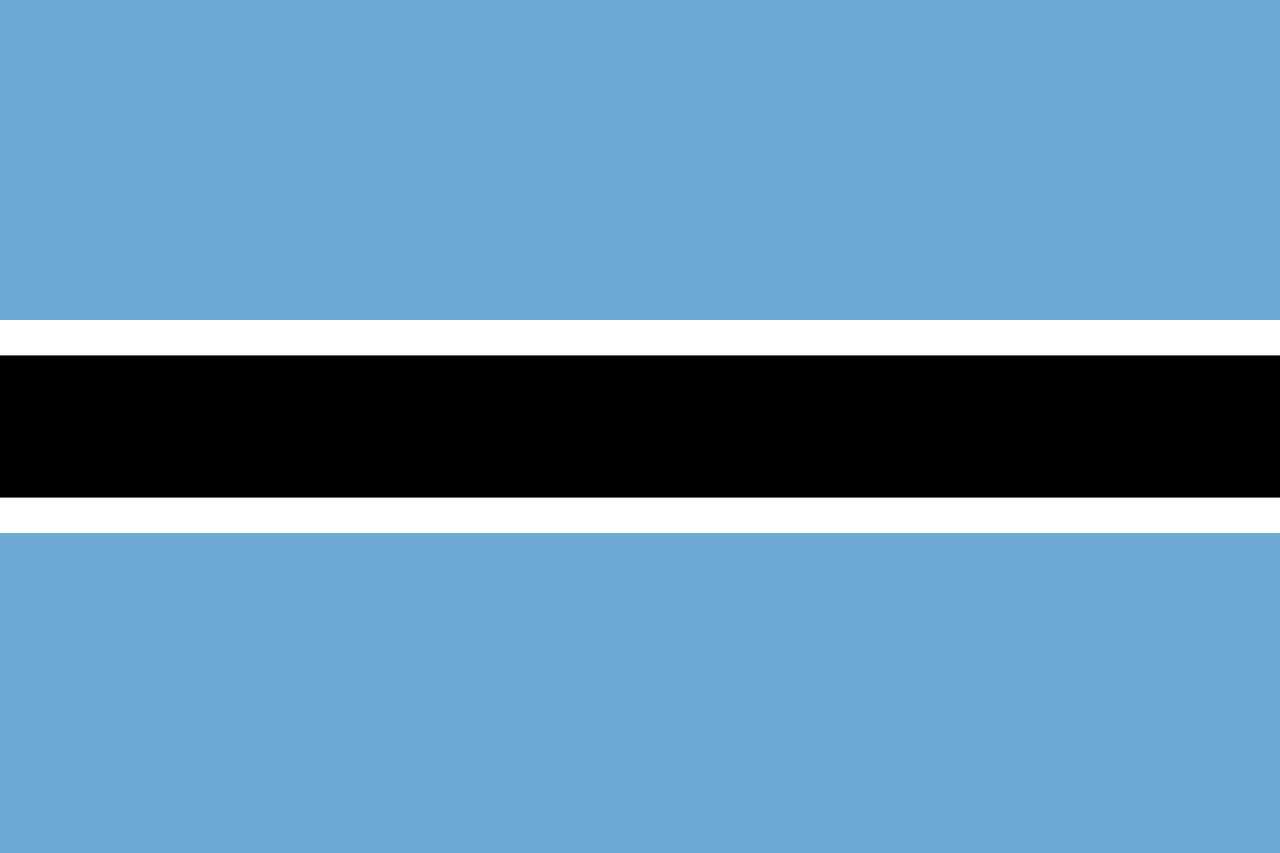
Botswana
Africa
Light blue field with a central black horizontal stripe bordered by thin white stripes, representing the life-giving rains, racial harmony, and the zebra that symbolizes the coexistence of black and white people in peace.
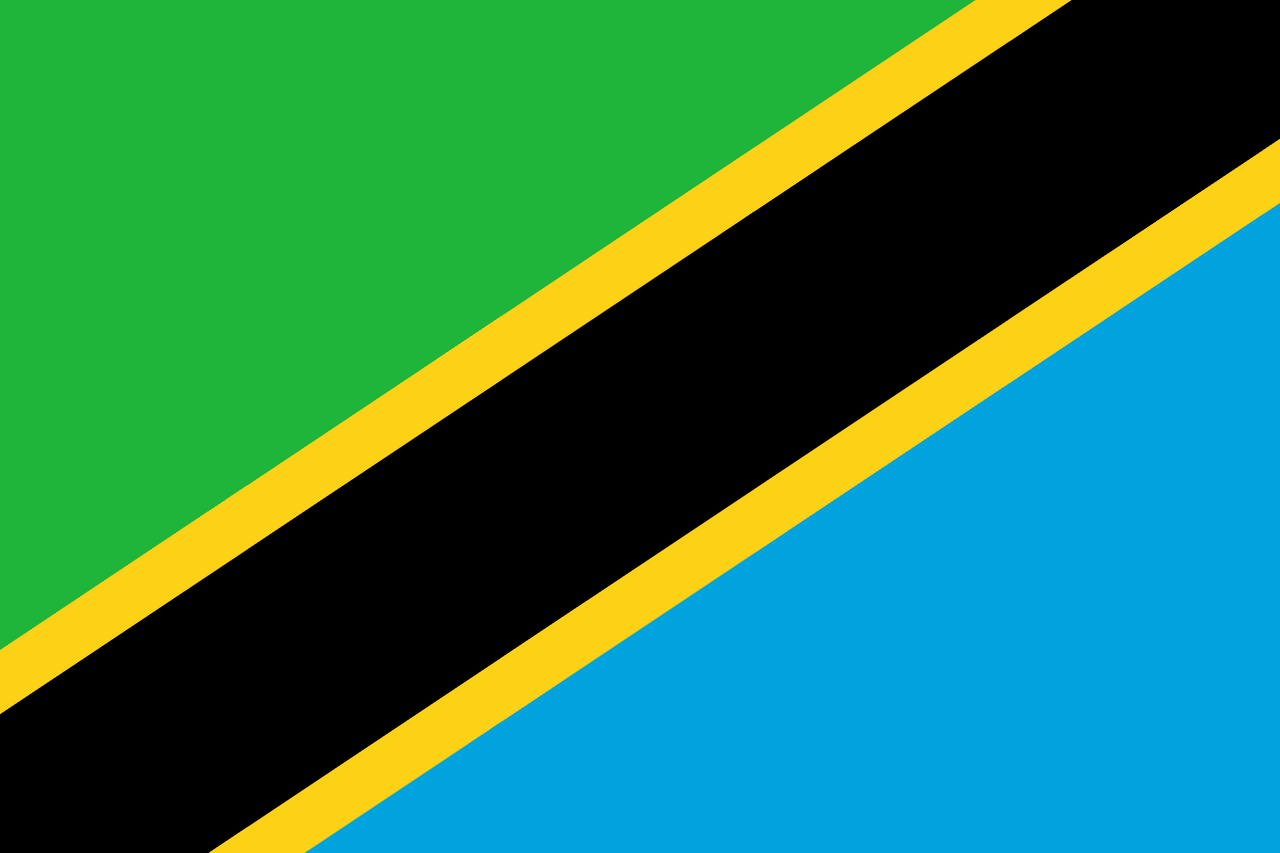
Tanzania
Africa
A green triangle in the upper hoist, a blue triangle in the lower fly, separated by a diagonal black stripe bordered by yellow stripes, representing the country's agriculture and forests, mineral wealth, the African people, and the Indian Ocean, symbolizing the union of Tanganyika and Zanzibar.

Angola
Africa
Two horizontal stripes of red and black with a yellow emblem in the center featuring a machete, star, and half gear wheel, representing the blood shed for independence, the African heritage, and the tools of liberation - agricultural work, socialism, and industrial progress.