Uganda Flag Meaning
Six horizontal stripes alternating black, yellow, and red (repeated twice) with a white circle containing the grey crowned crane in the center, representing the African people, sunshine and prosperity, brotherhood and unity, and the national bird that symbolizes Uganda's forward movement.
- Continent
- Africa
- Adopted
- 1962
- Ratio
- 2:3
- Colors
- black, yellow, red, white
- Designer
- Grace Ibingira

Symbolism
Black Stripes: Represent the African people and their heritage, symbolizing the indigenous population of Uganda and their connection to the broader African continent and shared struggles for independence.
Yellow Stripes: Represent the abundant sunshine that Uganda enjoys throughout the year and the prosperity that this brings, symbolizing the bright future and economic potential of the nation.
Red Stripes: Represent the brotherhood that binds all Ugandans together regardless of tribe or religion, as well as the blood that flows through all people, symbolizing unity and shared humanity.
White Circle: Represents peace and the purity of intentions of the Ugandan people, providing the background for the national symbol and expressing hope for harmony among all citizens.
Grey Crowned Crane: Represents Uganda's national bird and serves as the country's symbol, with one leg raised symbolizing the nation's forward movement and progress, while its gentle nature represents the peaceful aspirations of Uganda.
History
- Pre-Colonial Era: Various kingdoms including Buganda, Bunyoro, Ankole, and Toro dominated the region, developing sophisticated political systems, trade networks, and cultural traditions that continue to influence modern Uganda.
- 1862-1894: European explorers including John Speke and Henry Morton Stanley arrived, followed by Christian missionaries and eventually British colonial administrators seeking to control the source of the Nile.
- 1894-1962: The British Protectorate of Uganda was established, ruling through existing kingdoms while introducing cash crops like cotton and coffee, Christianity, and Western education systems.
- October 9, 1962: Uganda gained independence from Britain under Prime Minister Milton Obote, adopting the current flag and establishing a federal system that initially preserved traditional kingdoms.
- 1966: Obote abolished the kingdoms and declared himself executive president, beginning the erosion of democratic institutions and setting the stage for future political instability.
- January 25, 1971: Idi Amin seized power in a military coup, beginning eight years of brutal dictatorship that killed an estimated 300,000 people and expelled the entire Asian population.
- 1979: Tanzanian forces and Ugandan exiles overthrew Amin after his invasion of Tanzania, but political instability continued with weak governments and ongoing civil conflict.
- 1980-1985: Milton Obote returned to power through disputed elections, leading to the Bush War as Yoweri Museveni's National Resistance Army fought against government forces.
- January 26, 1986: Museveni's National Resistance Movement took power, promising democratic governance and beginning reconstruction after decades of conflict and economic collapse.
- 1986-2005: The Lord's Resistance Army insurgency in northern Uganda displaced over 1.5 million people and recruited thousands of child soldiers, creating one of Africa's worst humanitarian crises.
- 2005-Present: Multi-party democracy was restored, but Museveni has remained in power through multiple elections criticized as unfair, while Uganda has become increasingly authoritarian despite economic growth.
Trivia
- Uganda is often called the 'Pearl of Africa' due to its stunning natural beauty, including the source of the Nile River, snow-capped mountains, and diverse ecosystems supporting incredible wildlife.
- The flag represents one of the world's most biodiverse countries, home to more than half of the world's remaining mountain gorillas and over 1,000 bird species in an area smaller than Oregon.
- Uganda has over 40 different ethnic groups speaking more than 40 languages, with English as the official language and Swahili recognized as a second official language.
- The country is the source of the White Nile, with the river beginning at Lake Victoria (shared with Kenya and Tanzania) and flowing north through Sudan and Egypt to the Mediterranean.
- Uganda has one of the world's youngest populations, with over 75% under age 30, creating both opportunities for economic growth and challenges for employment and education.
- The flag flies over a country that has made significant progress in fighting HIV/AIDS, reducing infection rates from 30% in the 1980s to about 6% today through comprehensive prevention programs.
- Traditional kingdoms were restored in 1993 as cultural institutions without political power, allowing the Buganda, Bunyoro, Ankole, Toro, and Busoga peoples to maintain their heritage and ceremonies.
- Coffee is Uganda's main export crop and economic mainstay, with small-scale farmers producing both robusta and arabica varieties that generate crucial foreign exchange earnings.
- The country has discovered significant oil reserves in the western region, with production expected to begin in the mid-2020s, potentially transforming the economy if managed properly.
- Traditional music includes instruments like the adungu (harp), akogo (thumb piano), and various drums, while modern Ugandan music blends traditional rhythms with contemporary styles.
- Uganda has been a major refugee host, welcoming over 1.5 million refugees from South Sudan, Democratic Republic of Congo, and other neighboring countries affected by conflict.
- The flag represents a country where about 85% of the population practices Christianity (equally divided between Catholic and Protestant), with Islam and traditional religions also present.
- Traditional foods include matoke (steamed green bananas), posho (maize flour staple), groundnut sauce, and fresh fish from the country's many lakes and rivers.
- Despite natural wealth and resources, Uganda remains one of the world's poorest countries, with most of the population dependent on subsistence agriculture and facing challenges with corruption and weak institutions.
- The country has made progress in education, achieving near-universal primary enrollment, though quality remains a challenge, and efforts continue to expand access to secondary and higher education.
Related Countries
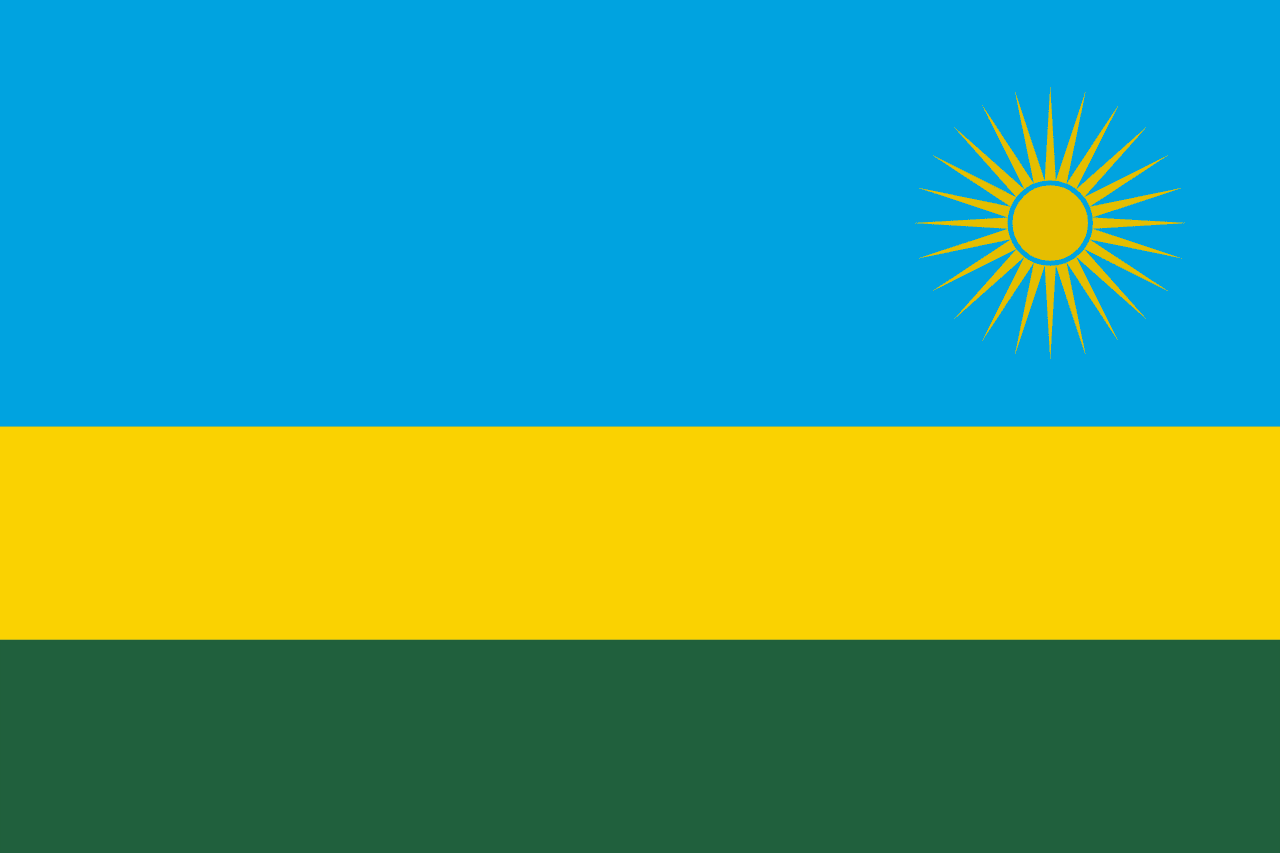

Rwanda
Africa
A tricolor of blue, yellow, and green bands with a golden sun in the upper fly corner. Adopted in 2001, the flag symbolizes unity, hope, and a new era of peace following the 1994 genocide.
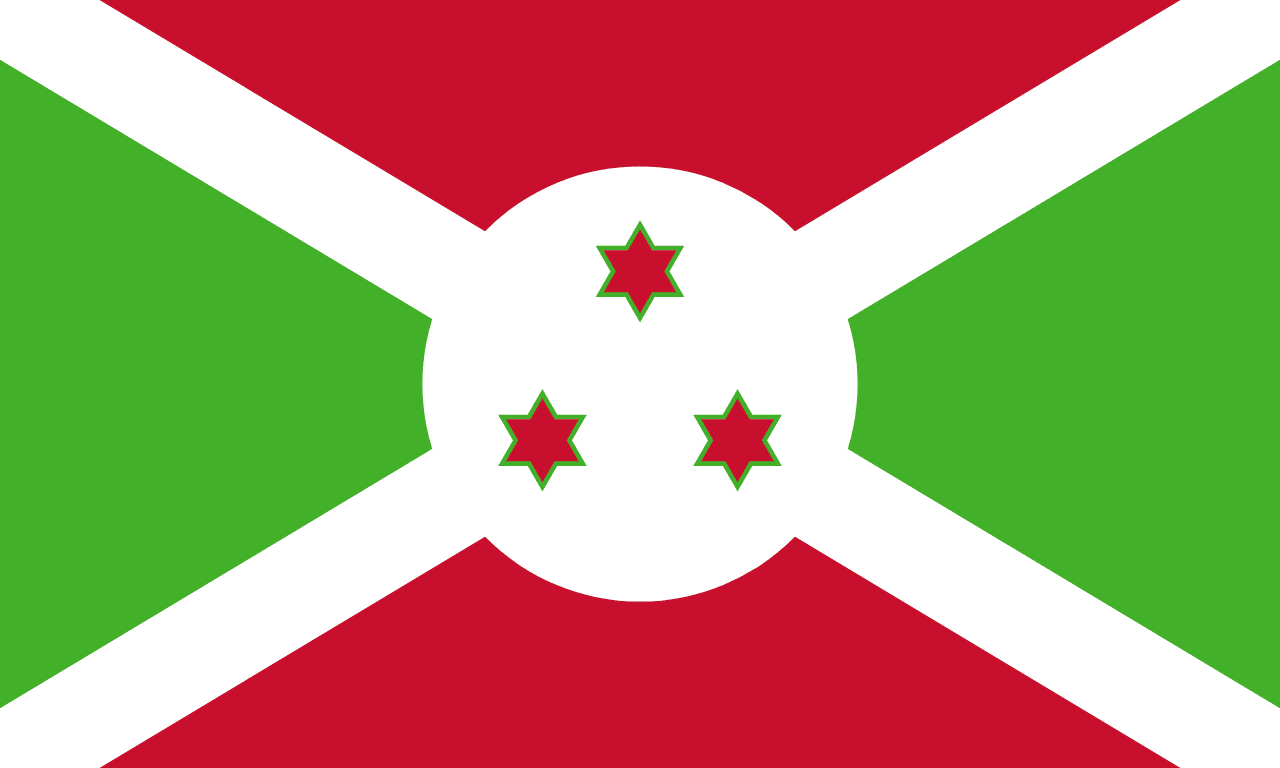
Burundi
Africa
A white diagonal cross dividing the flag into alternating red and green triangles, with three red stars outlined in green in the center circle, representing unity, work, progress, and the three ethnic groups of Burundi.
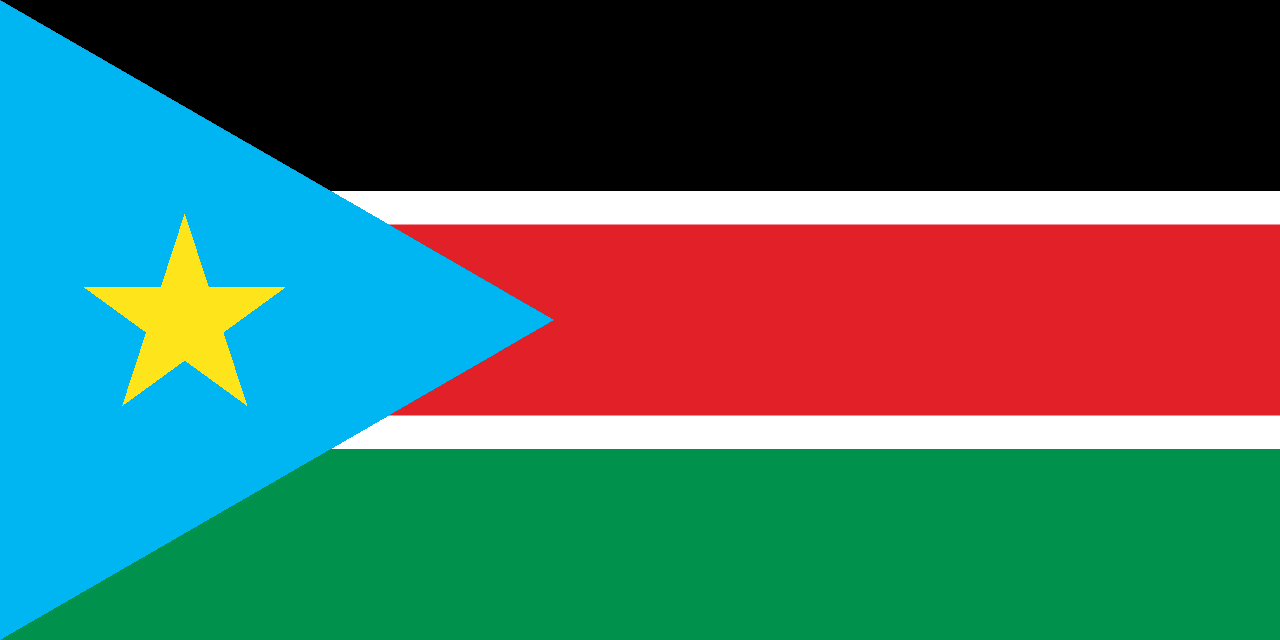
South Sudan
Africa
Three horizontal stripes of black, red, and white with a blue triangle at the hoist containing a yellow star, representing the African people, the blood shed for freedom, peace, the Nile River, and the unity of the states, designed for the world's newest country upon independence in 2011.
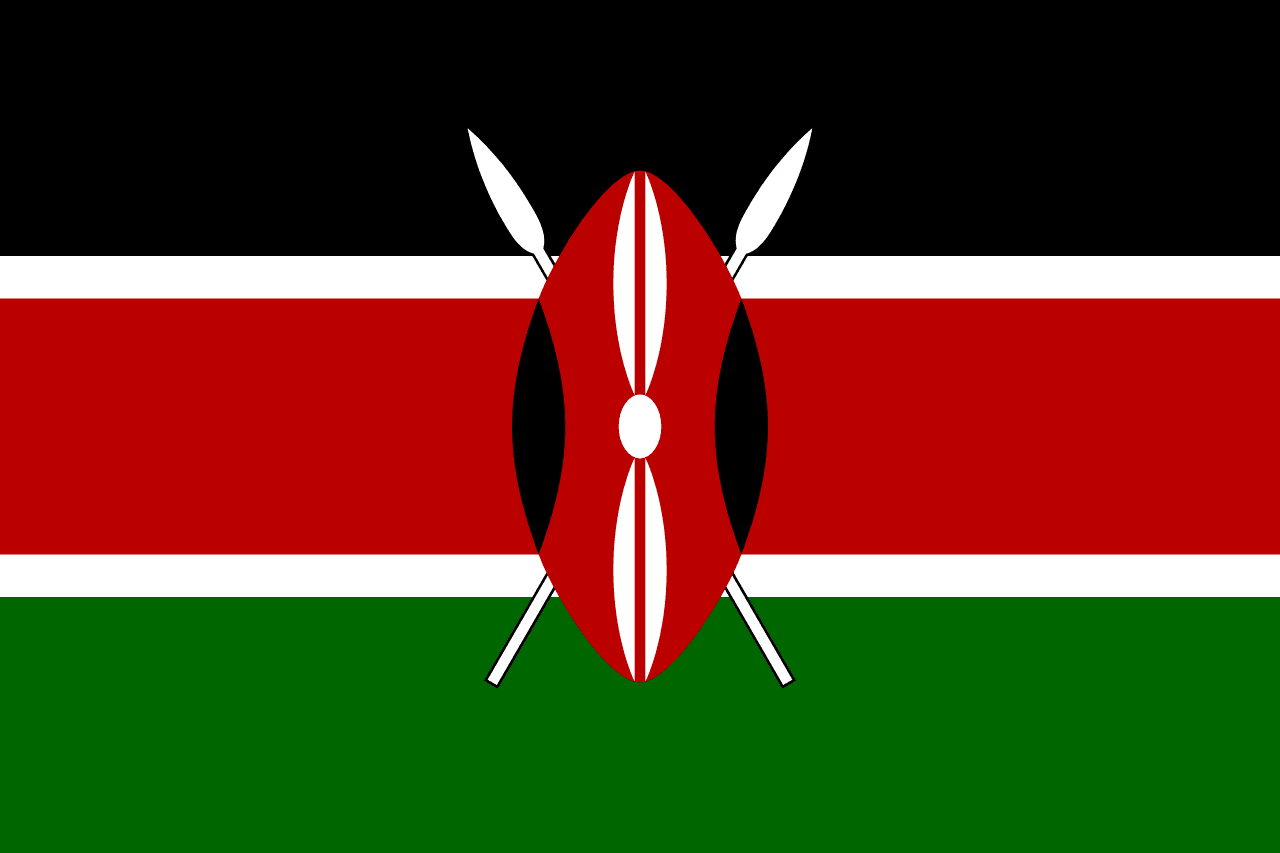
Kenya
Africa
Three horizontal stripes of black, red, and green separated by narrow white stripes, with a traditional Maasai shield and two crossed spears centered on the flag, representing Kenya's struggle for independence and the defense of freedom.
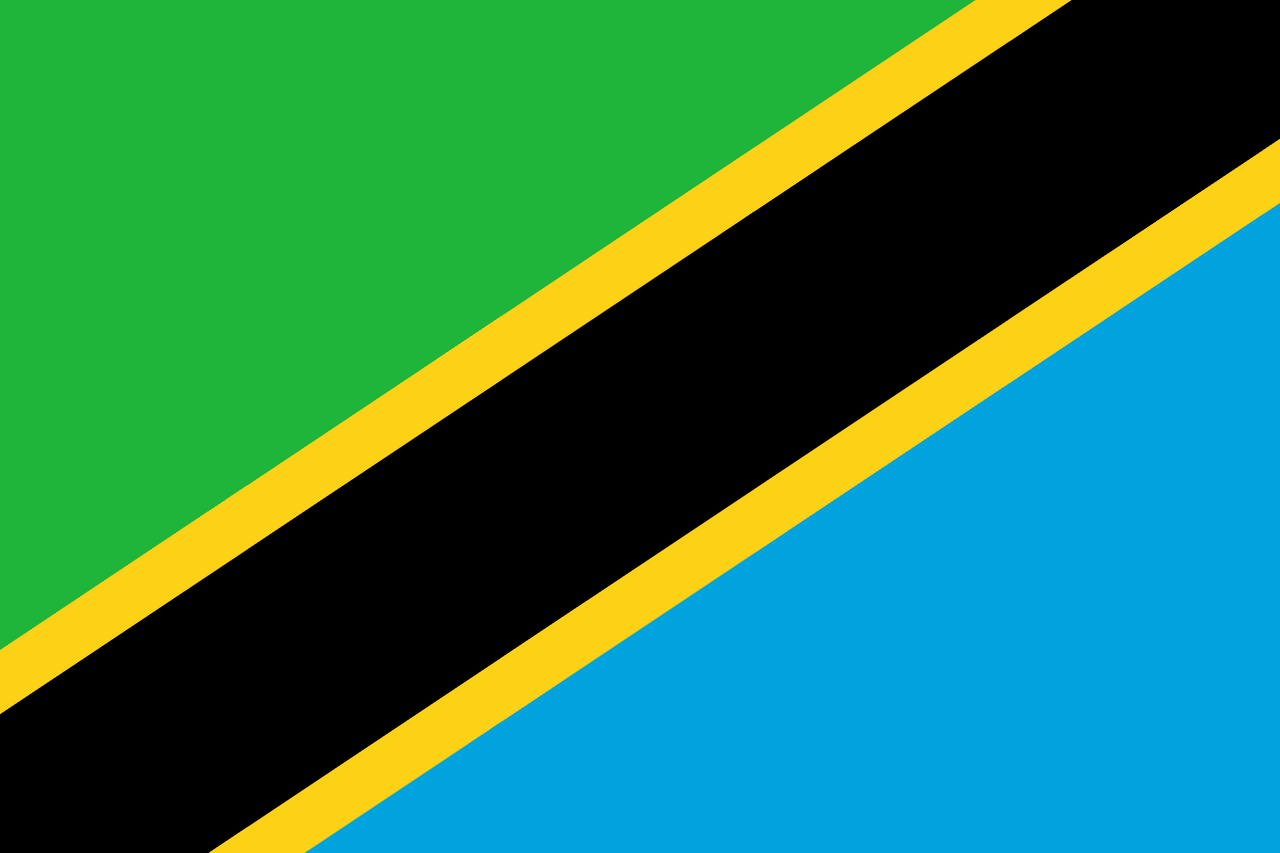
Tanzania
Africa
A green triangle in the upper hoist, a blue triangle in the lower fly, separated by a diagonal black stripe bordered by yellow stripes, representing the country's agriculture and forests, mineral wealth, the African people, and the Indian Ocean, symbolizing the union of Tanganyika and Zanzibar.

Ethiopia
Africa
Three horizontal stripes of green, yellow, and red with a blue circle containing a yellow five-pointed star in the center, representing the original Pan-African colors, the diversity and unity of Ethiopia's peoples, and the country's ancient independence.