United Arab Emirates Flag Meaning
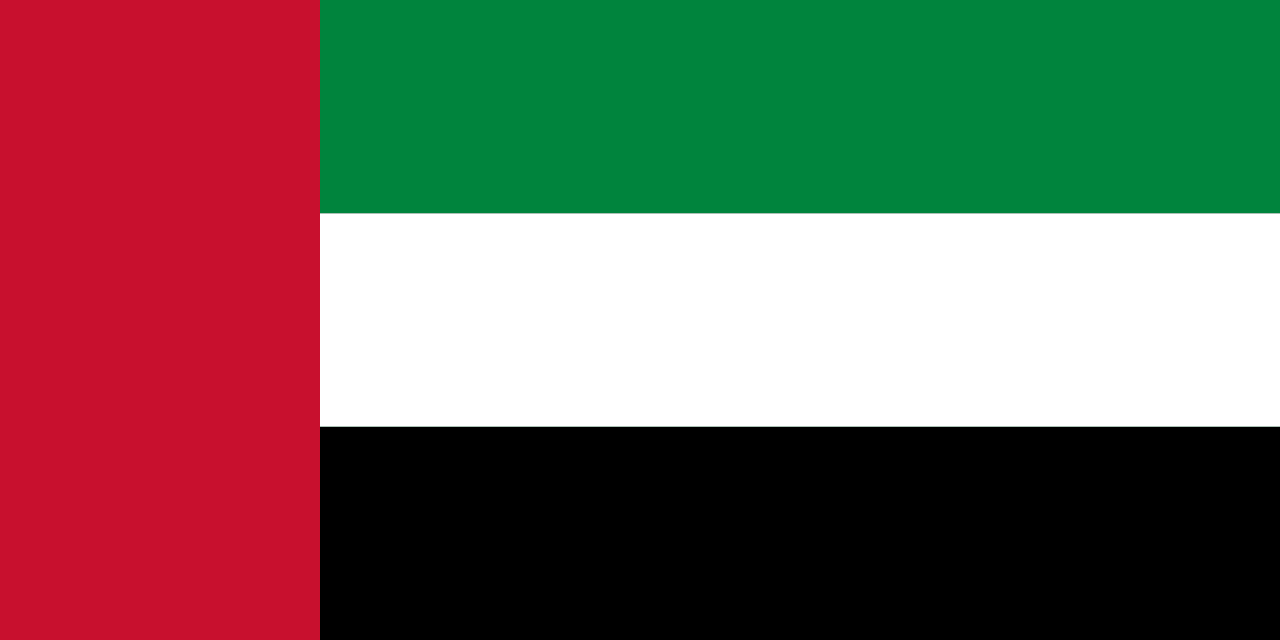
A vertical red stripe at the hoist with three horizontal stripes of green, white, and black on the fly side, representing the Pan-Arab colors that symbolize Arab unity, fertility, peace, and the defeat of enemies, designed by a young Emirati and chosen from over 1,000 submissions.
- Continent
- Asia
- Adopted
- 1971
- Ratio
- 1:2
- Colors
- red, white, black, green
- Designer
- Abdullah Mohammed Al Maainah

Symbolism
Red Stripe: Represents the sacrifices of previous generations and the courage of the UAE's leaders and people, symbolizing the strength and determination that built the modern federation from desert sheikhdoms.
Green Stripe: Represents fertility, growth, and prosperity, symbolizing the hope for continued development and the agricultural oases that sustained life in the harsh desert environment of the Arabian Peninsula.
White Stripe: Represents peace and honesty, symbolizing the peaceful intentions of the UAE toward all nations and the honest dealings that have made it a trusted partner in international business and diplomacy.
Black Stripe: Represents the defeat of enemies and the oil wealth that transformed the UAE, symbolizing both the historical struggles overcome and the black gold that enabled rapid modernization.
Pan-Arab Colors: The flag uses the traditional Arab colors that connect the UAE to the broader Arab world, expressing solidarity with Arab nationalism and shared cultural heritage.
History
- Pre-Islamic Era: The region was inhabited by various Arab tribes and served as an important trading post between Mesopotamia and the Indian Ocean, with archaeological evidence of settlements dating back 7,000 years.
- 7th Century: Islam arrived during the Prophet Muhammad's lifetime, with local tribes converting and the region becoming part of the expanding Islamic empire, establishing the religious foundation of Emirati identity.
- 1500s-1700s: Portuguese and later Ottoman influence in the Gulf region, while local Arab tribes including the Bani Yas developed pearl diving and trading economies that would sustain the coastal communities.
- 1820: The General Maritime Treaty with Britain established the Trucial States system, bringing British protection in exchange for agreements to end piracy and slavery in the Gulf.
- 1853-1971: The Perpetual Maritime Truce created the Trucial States under British protection, allowing local rulers to maintain internal autonomy while Britain controlled foreign affairs and defense.
- 1958-1962: Oil discovery in Abu Dhabi and later other emirates began the transformation from a subsistence economy based on pearling, fishing, and trade to oil-based wealth.
- 1968: Britain announced withdrawal from the Gulf, leading to negotiations among the Trucial States and neighboring Bahrain and Qatar about forming a federation.
- December 2, 1971: Six emirates (Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm al-Quwain, and Fujairah) formed the United Arab Emirates under President Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan, adopting the current flag.
- February 10, 1972: Ras al-Khaimah joined as the seventh emirate, completing the federation and establishing the modern boundaries of the UAE.
- 1970s-1990s: Rapid development using oil revenues transformed the UAE into a modern state with world-class infrastructure, while Dubai emerged as a regional business and tourism hub.
- 2000s-2010s: Economic diversification accelerated with Dubai becoming a global financial center, while Abu Dhabi invested oil wealth in sovereign wealth funds and renewable energy projects.
- 2020-Present: The Abraham Accords normalized relations with Israel, while the UAE has pursued space exploration, artificial intelligence, and sustainable development as part of its Vision 2071 strategy.
Trivia
- The UAE is a federation of seven emirates, each with its own ruler, but Abu Dhabi is by far the largest and wealthiest, containing about 87% of the country's land area.
- The flag represents one of the world's wealthiest countries per capita, with the UAE having successfully diversified its economy beyond oil into finance, tourism, and technology.
- Dubai is home to the world's tallest building (Burj Khalifa), largest shopping mall (Dubai Mall), and one of the busiest international airports, making it a global hub for business and tourism.
- Arabic is the official language, but English is widely used in business and education, while the country hosts expatriates from over 190 countries, making up about 85% of the population.
- The UAE has no income tax for individuals and very low corporate taxes, making it an attractive destination for international businesses and wealthy individuals.
- The flag flies over a country that has transformed from a collection of desert sheikhdoms dependent on pearling and fishing to a modern nation in just 50 years.
- Traditional Emirati culture includes camel racing, falconry, and Bedouin poetry, though these coexist with ultramodern cities and international cultural influences.
- The UAE is investing heavily in renewable energy, including the world's largest single-site solar park (Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park) as part of its sustainability goals.
- Women in the UAE have achieved significant advancement, comprising 70% of university graduates and holding important positions in government and business, including cabinet ministers.
- The country has successfully launched its first astronaut program and Mars mission (Hope Probe), positioning itself as a leader in space exploration in the Arab world.
- Traditional architecture includes wind towers and courtyard houses adapted to the desert climate, while modern UAE architecture features some of the world's most innovative and iconic buildings.
- The UAE is home to the Louvre Abu Dhabi, the first universal museum in the Arab world, demonstrating the country's commitment to cultural development and soft power.
- Emirati cuisine blends Arab, Persian, Indian, and African influences, with dishes like machboos (spiced rice), luqaimat (sweet dumplings), and shawarma being popular.
- The flag represents a country that has become a major humanitarian aid donor, consistently ranking among the world's most generous nations in terms of aid as a percentage of GDP.
- Despite rapid modernization, the UAE maintains strong tribal and family traditions, with majlis (council) meetings where citizens can directly petition rulers continuing to play important roles in governance.
Related Countries
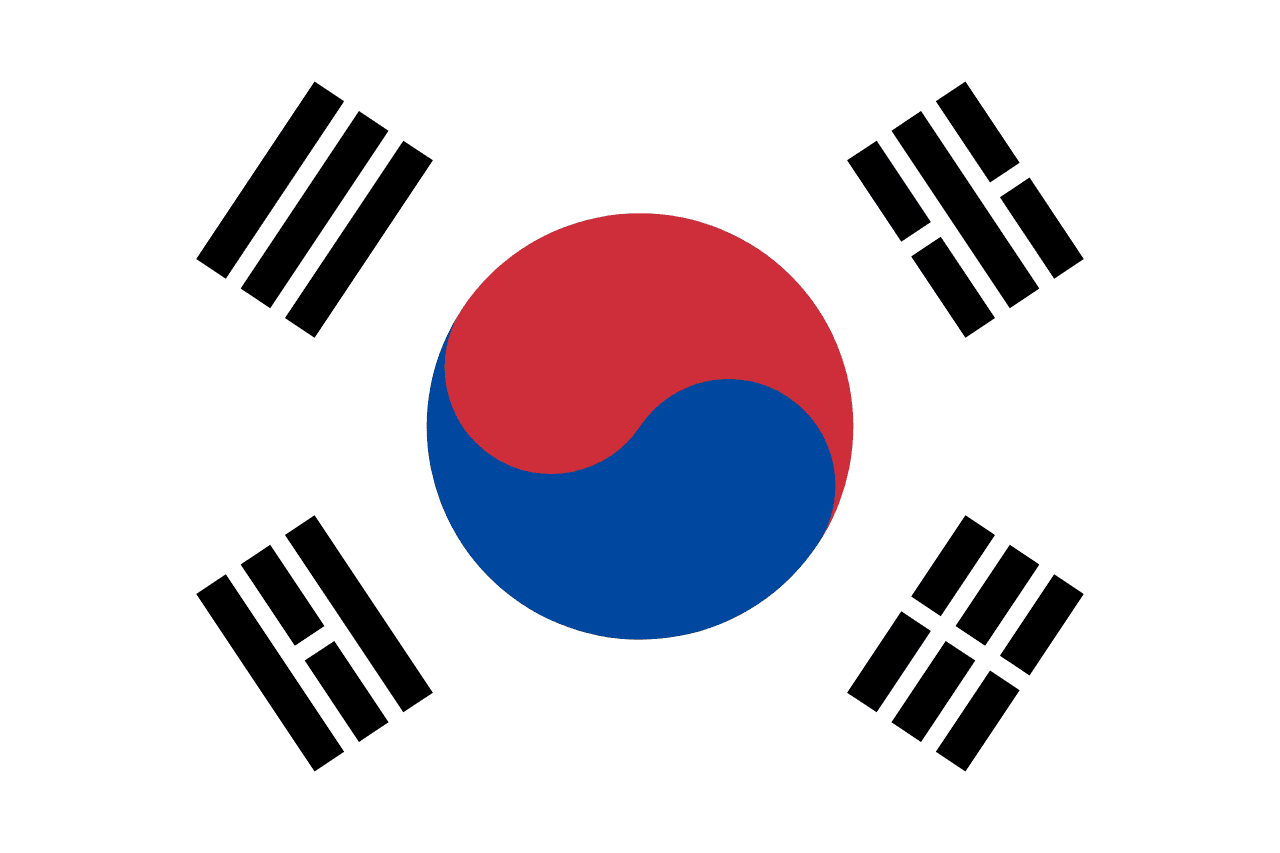
South Korea
Asia
A white field with a red and blue taegeuk (yin-yang symbol) in the center surrounded by four black trigrams from the I Ching, representing the harmony of opposites, the balance of natural forces, and the philosophical foundations of Korean civilization dating back thousands of years.
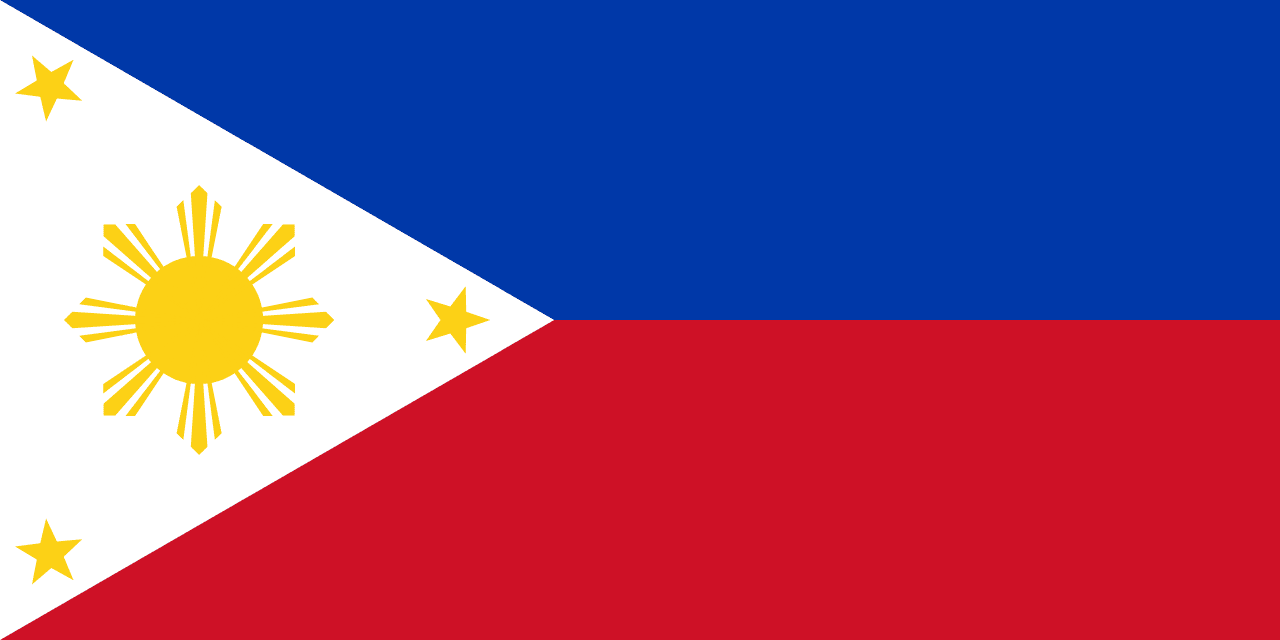
Philippines
Asia
A horizontal bicolor of blue over red with a white equilateral triangle at the hoist, containing a golden sun and three golden stars. The Philippine flag is unique in that it is inverted in wartime, with the red field displayed on top.
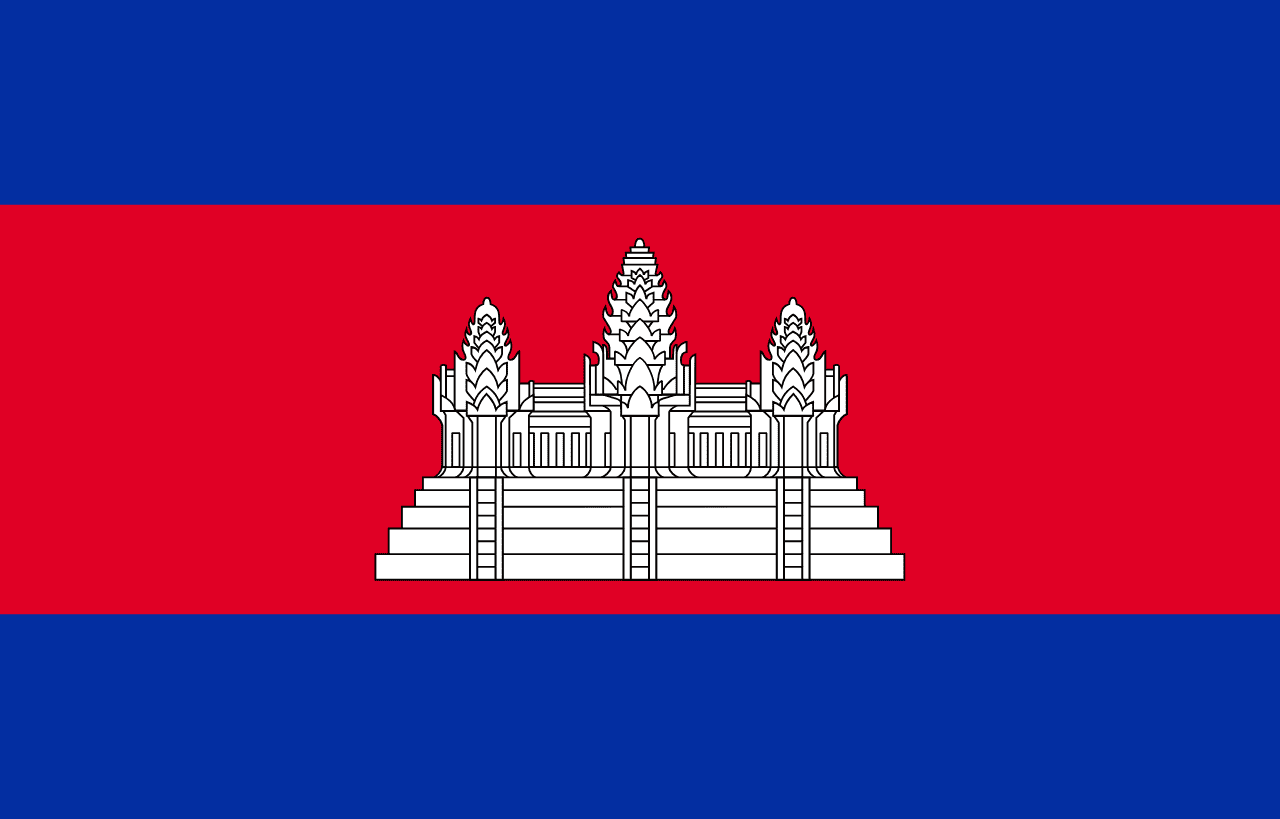
Cambodia
Asia
Three horizontal stripes of blue, red (double width), and blue with a white depiction of Angkor Wat temple in the center, representing the nation, the king, and the sacred temple that symbolizes Cambodia's glorious past and cultural heritage.
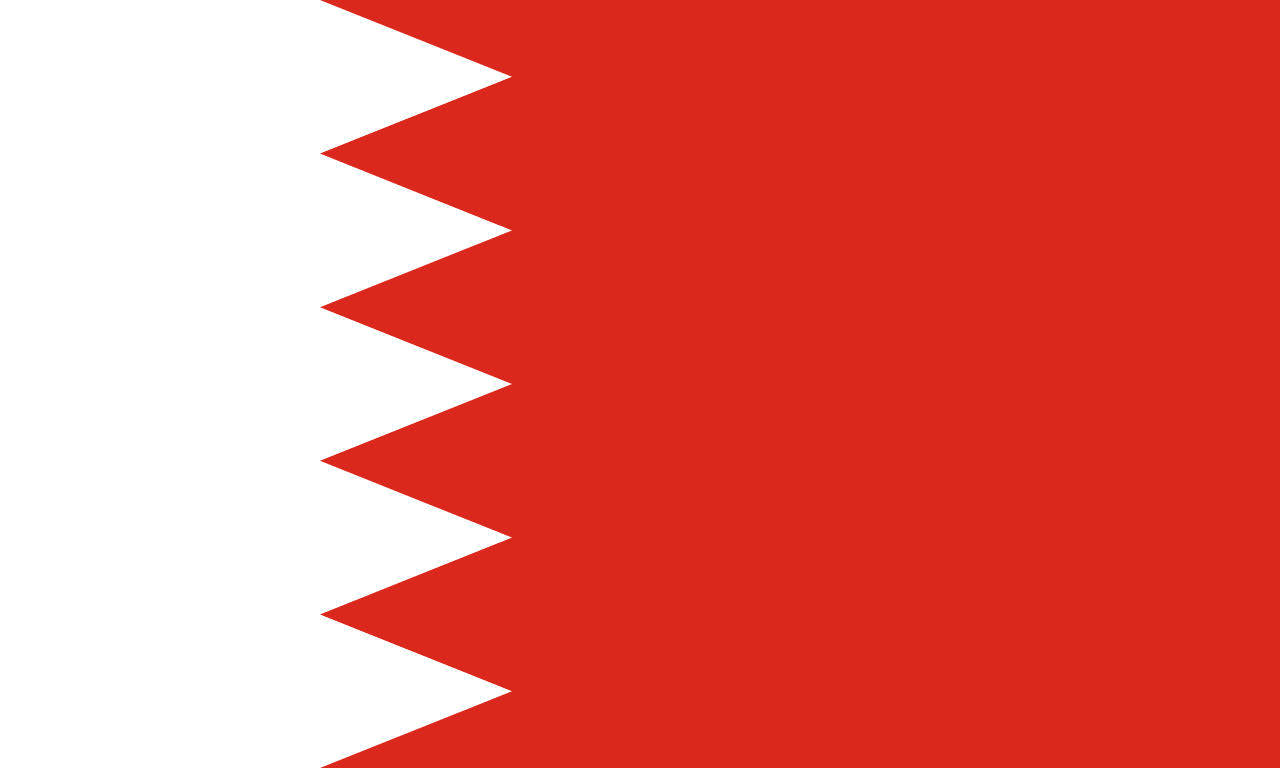

Bahrain
Asia
A white band on the hoist side separated from a red field by a serrated line with five triangular points, representing peace and the five pillars of Islam, while the red represents the Kharijite sect of Islam that historically dominated the region.

Brunei
Asia
A yellow field with two diagonal stripes of white and black, featuring the national coat of arms in red in the center, representing the Sultan's sovereignty, the state's prosperity, and the nation's commitment to peace and Islamic values.
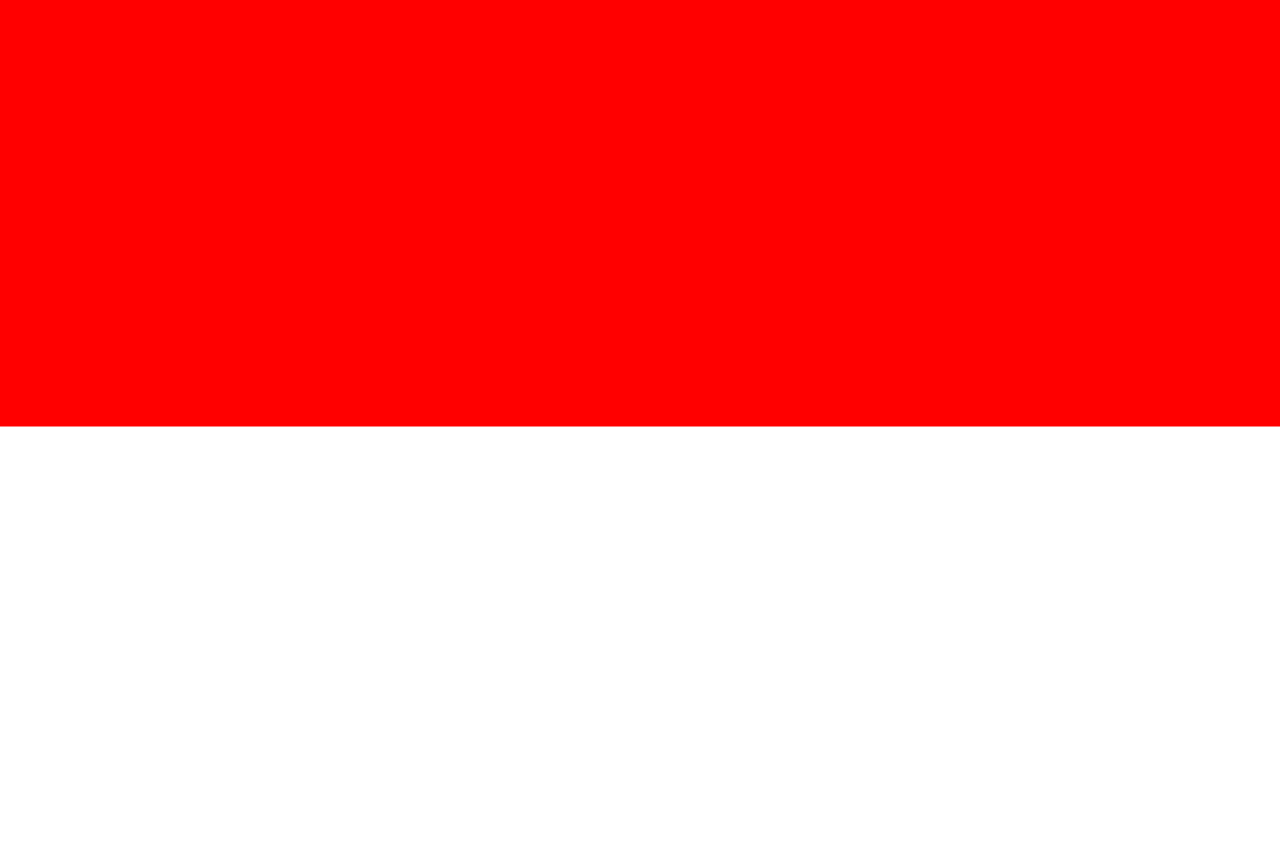

Indonesia
Asia
Two horizontal stripes of red over white, known as 'Sang Saka Merah-Putih' (The Sacred Red and White), representing the courage and purity of the Indonesian people and their struggle for independence from colonial rule.