Brunei Flag Meaning
A yellow field with two diagonal stripes of white and black, featuring the national coat of arms in red in the center, representing the Sultan's sovereignty, the state's prosperity, and the nation's commitment to peace and Islamic values.
- Continent
- Asia
- Adopted
- 1959
- Ratio
- 1:2
- Colors
- yellow, black, white, red
- Designer
- Unknown

Symbolism
Yellow Field: Represents the Sultan and the royal color of Brunei, symbolizing the absolute monarchy that has ruled for over 600 years and the prosperity brought by the nation's oil and gas wealth.
Black Stripe: Represents the chief minister (Perdana Menteri) and the wisdom of governance, symbolizing the administrative structure that supports the Sultan's rule and the nation's commitment to good governance.
White Stripe: Represents the religious council (Majlis Ugama) and the purity of Islam, symbolizing the nation's commitment to Islamic values and the spiritual guidance that shapes Bruneian society.
National Emblem: Features a crescent moon, parasol, hands, and Arabic script reading 'Always in service with God's guidance,' representing Islamic faith, royal protection, the helping hands of government, and divine blessing.
History
- 14th-16th Century: The Brunei Sultanate reached its golden age under Sultan Bolkiah, controlling much of Borneo and the southern Philippines, becoming a major trading power in Southeast Asia.
- 16th-19th Century: European colonial expansion and internal conflicts gradually reduced Brunei's territory and influence, with the sultanate ceding lands to the British North Borneo Company and the White Rajahs of Sarawak.
- 1888: Brunei became a British protectorate under the Treaty of Protection, allowing the Sultan to retain internal sovereignty while Britain controlled foreign affairs and defense.
- 1906: The British Residential system was established, giving the British Resident significant control over Brunei's administration while preserving the Sultan's ceremonial role.
- 1929: Oil was discovered in Seria, transforming Brunei's economy and providing the wealth that would later make it one of the richest nations per capita in the world.
- 1941-1945: Japanese occupation during World War II disrupted British rule, with the Sultan and royal family living under Japanese control until liberation by Australian forces.
- September 29, 1959: Brunei adopted its constitution and the current flag design, establishing internal self-government while remaining a British protectorate, with Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddin III modernizing the state.
- December 8, 1962: The Brunei Revolt, supported by Indonesia and opposing federation with Malaysia, was suppressed by British forces, leading to a state of emergency that lasted until 1984.
- January 1, 1984: Brunei gained full independence from Britain under Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah, becoming the last Southeast Asian nation to achieve independence and maintaining the 1959 flag design.
- 1990s-2000s: Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah implemented the 'Melayu Islam Beraja' (Malay Islamic Monarchy) ideology, emphasizing Malay culture, Islamic values, and monarchical traditions as the foundation of national identity.
- 2014: Brunei implemented Sharia law penal code, making it the first Southeast Asian country to do so at the national level, sparking international controversy and diplomatic tensions.
- 2019-Present: Following international pressure, Brunei extended a moratorium on the death penalty, while continuing to balance traditional Islamic governance with modern economic development and international relations.
Trivia
- Brunei is one of the wealthiest countries in the world per capita, primarily due to vast oil and natural gas reserves that fund a generous welfare state.
- The Sultan of Brunei owns one of the world's largest car collections, with thousands of luxury vehicles including custom Rolls-Royces and Ferraris.
- The flag represents a country where citizens pay no income tax and receive free healthcare and education through university level, funded by oil revenues.
- Brunei is one of the smallest countries in the world by land area and population, with only about 430,000 people living in an area smaller than Delaware.
- The official language is Malay, but English is widely spoken due to the British colonial legacy and is used in business and higher education.
- Kampong Ayer, the 'Venice of the East,' is a historic water village in Bandar Seri Begawan where about 30,000 people live in stilted houses over the Brunei River.
- The flag flies over a country that is one of the last absolute monarchies in the world, where the Sultan serves as both head of state and head of government.
- Brunei has one of the highest car ownership rates in the world, with virtually no public transportation and heavily subsidized gasoline.
- The country is famous for its pristine rainforests, with about 70% of its territory covered by primary tropical rainforest protected by strict conservation laws.
- Ulu Temburong National Park is often called the 'Green Jewel of Brunei' and contains some of the most pristine rainforest in Southeast Asia.
- Brunei follows a unique blend of Islamic law and English common law, reflecting its cultural heritage and colonial history.
- The flag represents a country where alcohol is prohibited and drug trafficking carries the death penalty under strict Islamic-influenced laws.
- Despite its small size, Brunei has significant geopolitical importance due to its strategic location along major shipping routes in the South China Sea.
- The Royal Regalia Museum houses one of the world's most impressive collections of royal artifacts, including the crown jewels and ceremonial items of the Sultan.
- Brunei maintains a policy of neutrality in international affairs while being a member of ASEAN and maintaining close ties with both Malaysia and Singapore.
Related Countries

Indonesia
Asia
Two horizontal stripes of red over white, known as 'Sang Saka Merah-Putih' (The Sacred Red and White), representing the courage and purity of the Indonesian people and their struggle for independence from colonial rule.
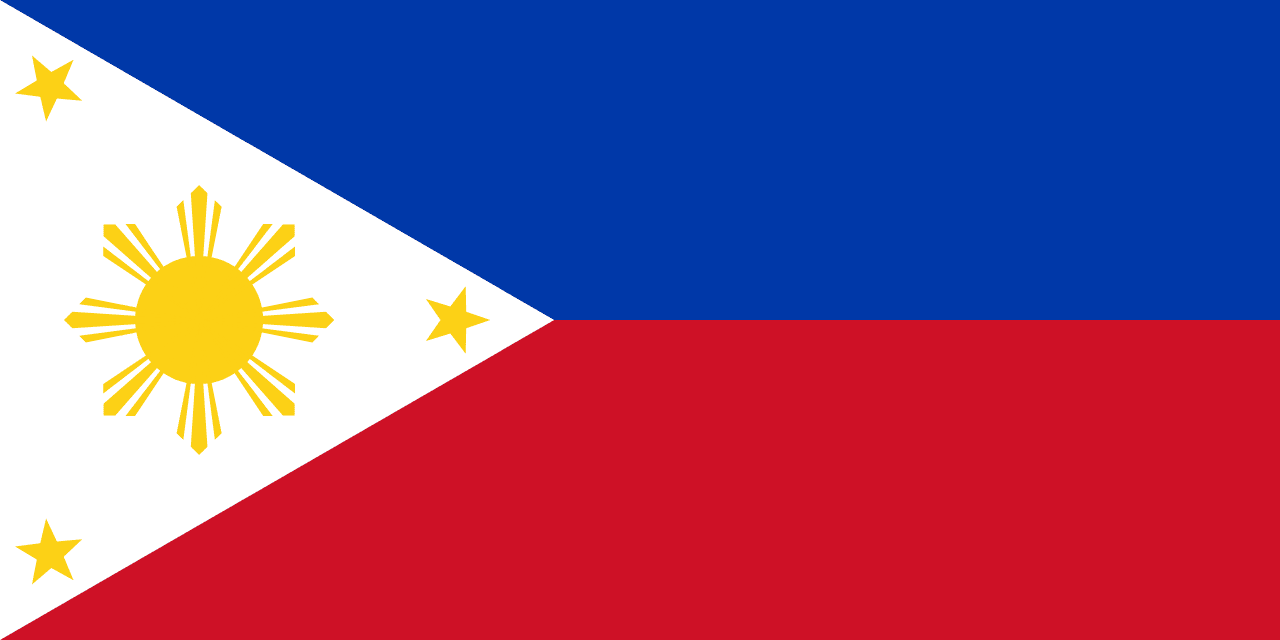
Philippines
Asia
A horizontal bicolor of blue over red with a white equilateral triangle at the hoist, containing a golden sun and three golden stars. The Philippine flag is unique in that it is inverted in wartime, with the red field displayed on top.

Singapore
Asia
A bicolor flag with a red upper half and white lower half. In the upper hoist is a white crescent moon beside five white five-pointed stars arranged in a circle. The flag symbolizes Singapore’s ideals of unity, progress, and multicultural harmony.

Vietnam
Asia
A red field with a large yellow five-pointed star in the center, representing the blood shed for independence and the unity of workers, peasants, intellectuals, youth, and soldiers under Communist Party leadership in the struggle for national liberation and socialist construction.
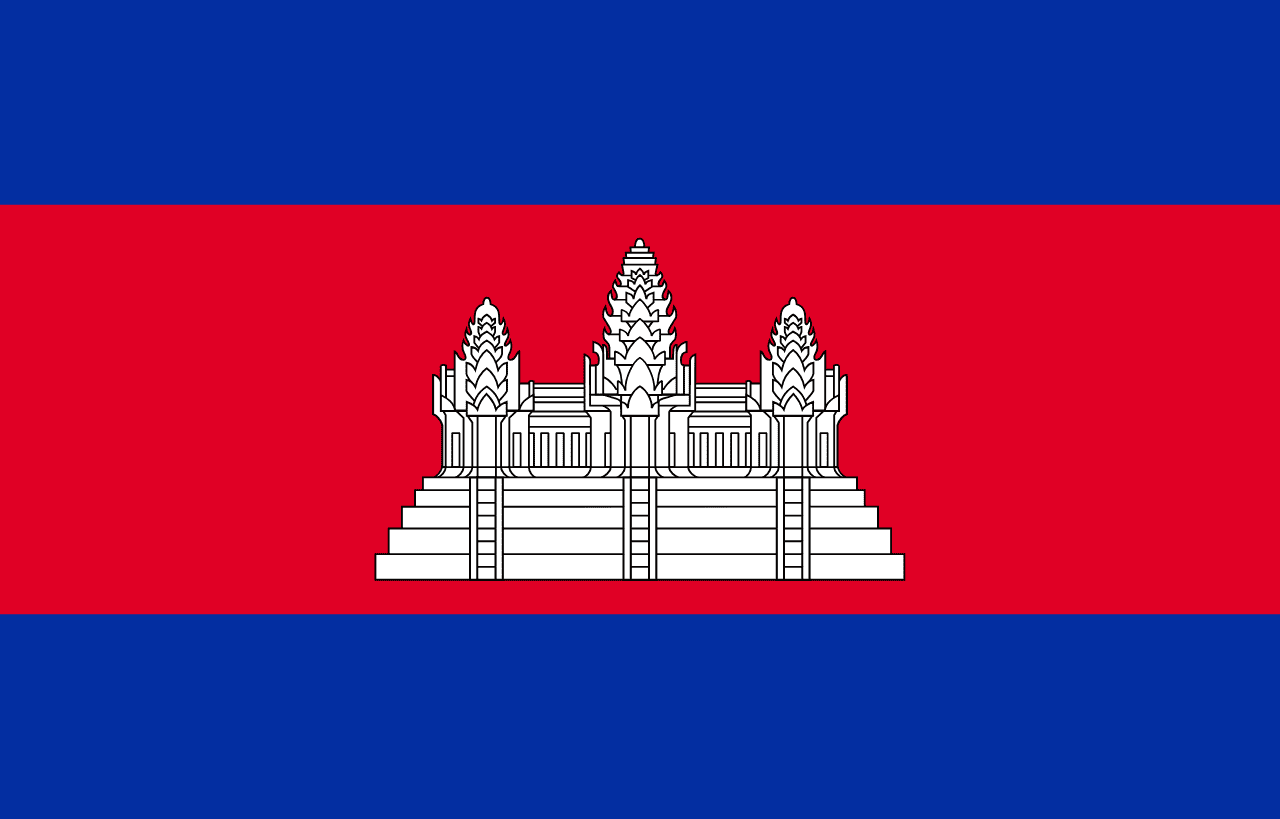
Cambodia
Asia
Three horizontal stripes of blue, red (double width), and blue with a white depiction of Angkor Wat temple in the center, representing the nation, the king, and the sacred temple that symbolizes Cambodia's glorious past and cultural heritage.
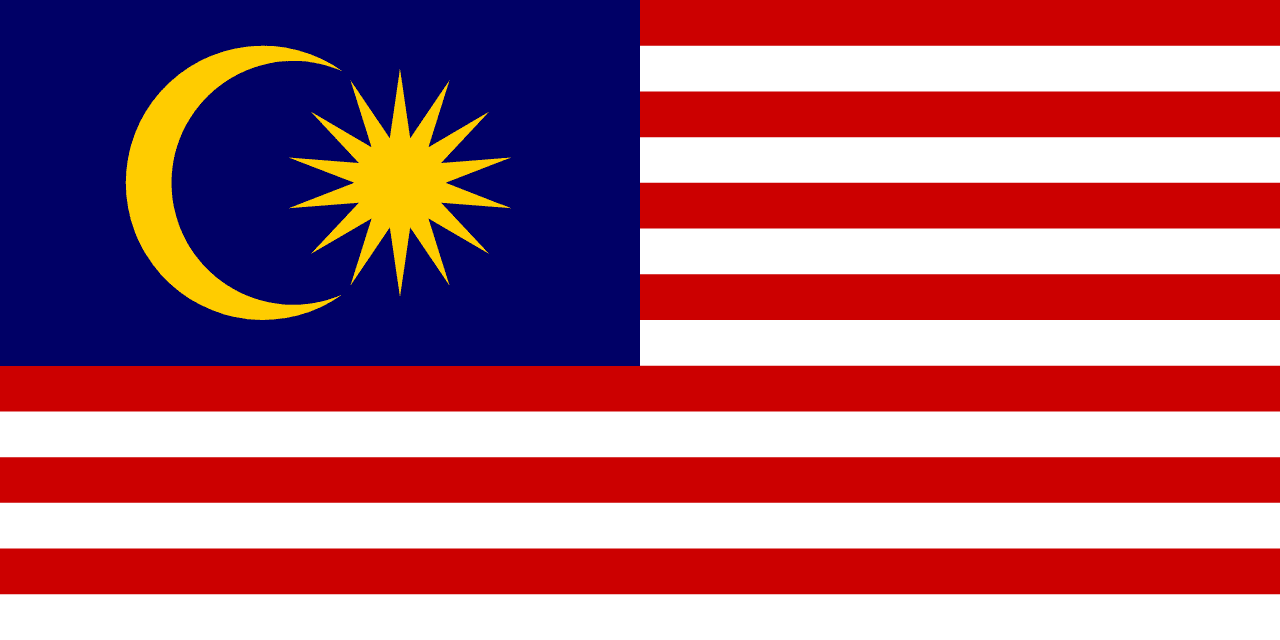
Malaysia
Asia
Fourteen alternating red and white stripes with a blue canton containing a yellow crescent and 14-pointed star, representing the federation of Malaysian states and territories united under Islam and royal authority.