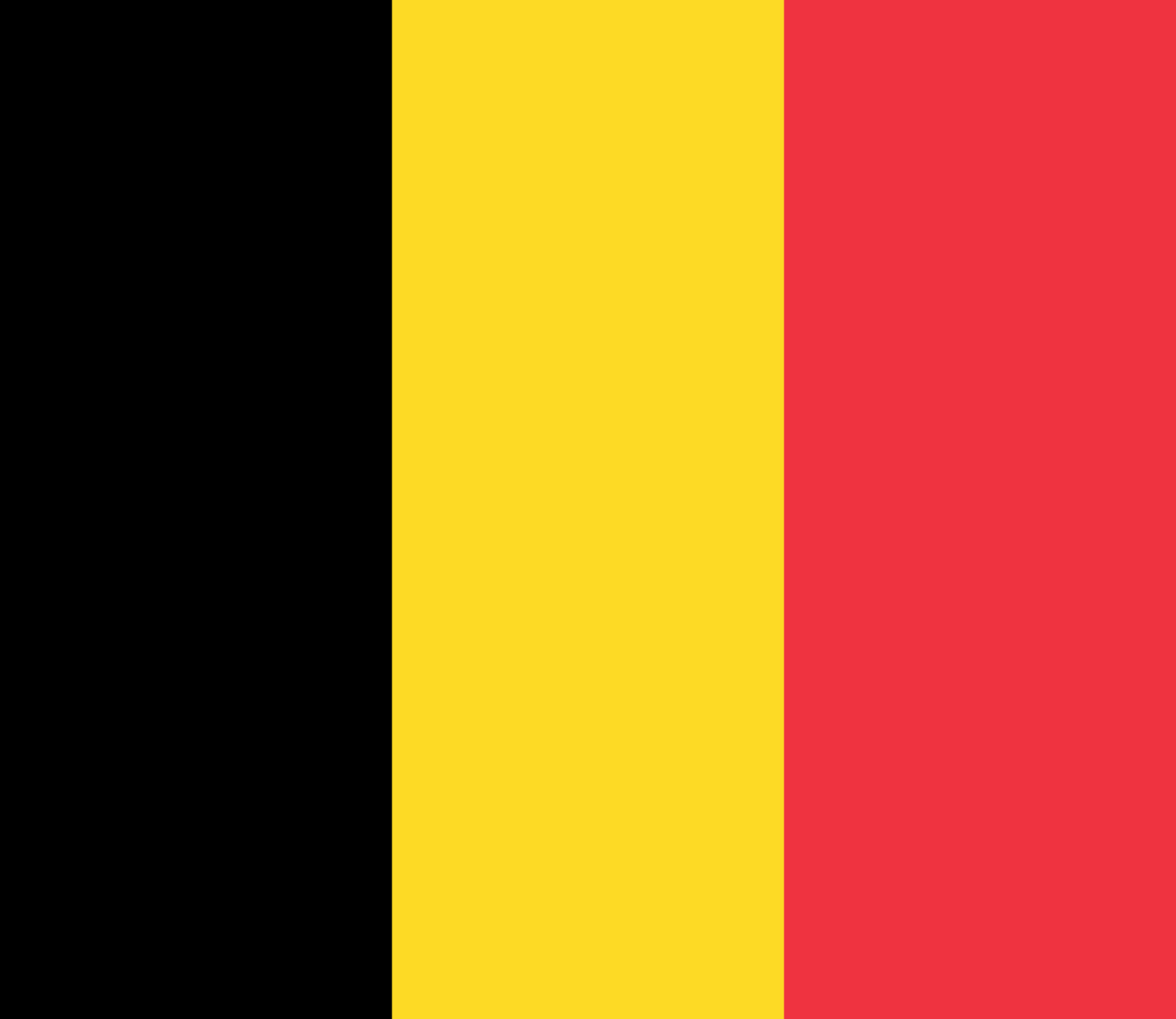
Belgium Flag Meaning
Three vertical stripes of black, yellow, and red derived from the coat of arms of the Duchy of Brabant, adopted during Belgium's independence revolution and representing the nation's determination, generosity, and sacrifice.
- Continent
- Europe
- Adopted
- 1831
- Ratio
- 13:15
- Colors
- black, yellow, red

Symbolism
Black Stripe: Represents the shield of the Duchy of Brabant's coat of arms and symbolizes determination, strength, and the resolve of the Belgian people during their struggle for independence.
Yellow Stripe: Derives from the gold lion of Brabant's heraldry and represents generosity, nobility, and the prosperity that Belgium sought to achieve as an independent nation.
Red Stripe: Comes from the red claws and tongue of the Brabant lion and symbolizes courage, valor, and the blood shed by those who fought for Belgian independence.
Vertical Arrangement: The vertical stripes distinguish Belgium's flag from similar tricolors and reflect the French revolutionary tradition that inspired the Belgian independence movement.
Brabant Heritage: The color combination honors the historic Duchy of Brabant, which included Brussels and much of central Belgium, connecting the modern state to its medieval roots.
History
- 12th Century: The Duchy of Brabant established its coat of arms featuring a gold lion with red claws and tongue on a black field, providing the colors for the future Belgian flag.
- 1789-1790: During the Brabant Revolution against Austrian rule, revolutionaries used black, yellow, and red cockades and banners, establishing these colors as symbols of Belgian resistance.
- 1815-1830: Belgium was united with the Netherlands under the Kingdom of the Netherlands, using Dutch symbols and suppressing Belgian cultural identity and Catholic traditions.
- August 25, 1830: The Belgian Revolution began in Brussels, with revolutionaries adopting black, yellow, and red as their colors, initially in horizontal stripes similar to the Dutch flag arrangement.
- September 1830: Revolutionary forces switched to vertical stripes to distance themselves from the Dutch horizontal tricolor and align with French revolutionary traditions.
- January 23, 1831: The National Congress officially adopted the black, yellow, and red tricolor as the national flag of the newly independent Kingdom of Belgium.
- 1831-Present: The flag has remained unchanged since adoption, surviving two world wars, German occupations, and various political changes while maintaining its symbolic importance.
Trivia
- Belgium's flag is often confused with Germany's flag, but Belgium uses vertical stripes (black-yellow-red) while Germany uses horizontal stripes (black-red-gold).
- The official ratio is 13:15, making it one of the few national flags that is nearly square, though it's often displayed in the more common 2:3 ratio.
- During the 1830 revolution, some early versions had horizontal stripes, but these were quickly changed to vertical to differentiate from the Dutch flag.
- The colors black, yellow, and red appear in the flags of several other European regions and countries, often tracing back to medieval heraldic traditions.
- Belgium's flag inspired the flags of several African nations, particularly those colonized by Belgium, including the Democratic Republic of Congo (formerly Zaire).
- The Brabant lion that inspired the flag colors still appears in the coat of arms of Belgium and several Belgian provinces and municipalities.
- During World War I and II, the Belgian flag became a symbol of resistance against German occupation, with citizens secretly displaying it despite prohibitions.
- The flag protocol requires the black stripe to be closest to the flagpole when displayed vertically, distinguishing it from similar tricolors.
- Belgian racing drivers and Formula 1 teams often use the national colors in their liveries, making the black-yellow-red combination recognizable in international motorsports.
- The European Union was partly inspired by Belgian federalism, and EU institutions in Brussels often display the Belgian flag alongside the European flag.
- Some Belgian political movements have proposed alternative flag designs, but the 1831 tricolor remains deeply embedded in national identity and tradition.
- The flag appears on Belgian euro coins and is featured prominently during National Day celebrations on July 21st, commemorating the first king's oath.
- Belgian chocolate companies and beer brewers often incorporate the flag colors into their packaging, making them symbols of Belgian culinary excellence worldwide.
- The flag flies at half-mast on specific memorial dates, including November 11 (Armistice Day) and during national mourning periods declared by the government.
- Unlike some national flags with complex meanings, Belgium's flag colors have remained consistent in their interpretation since 1831, reflecting the stability of their symbolism.
Related Countries
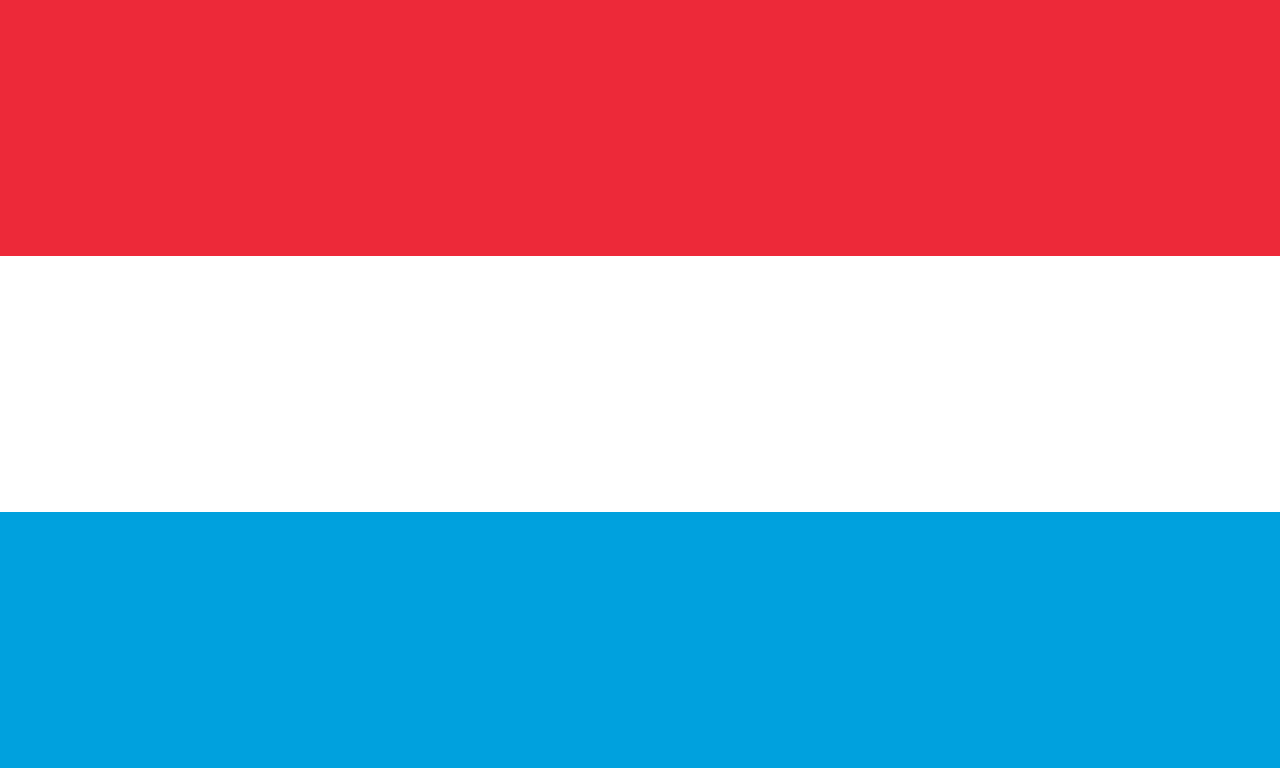

Luxembourg
Europe
Three horizontal stripes of red, white, and light blue representing the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, one of Europe's smallest but wealthiest nations and a founding member of the European Union.
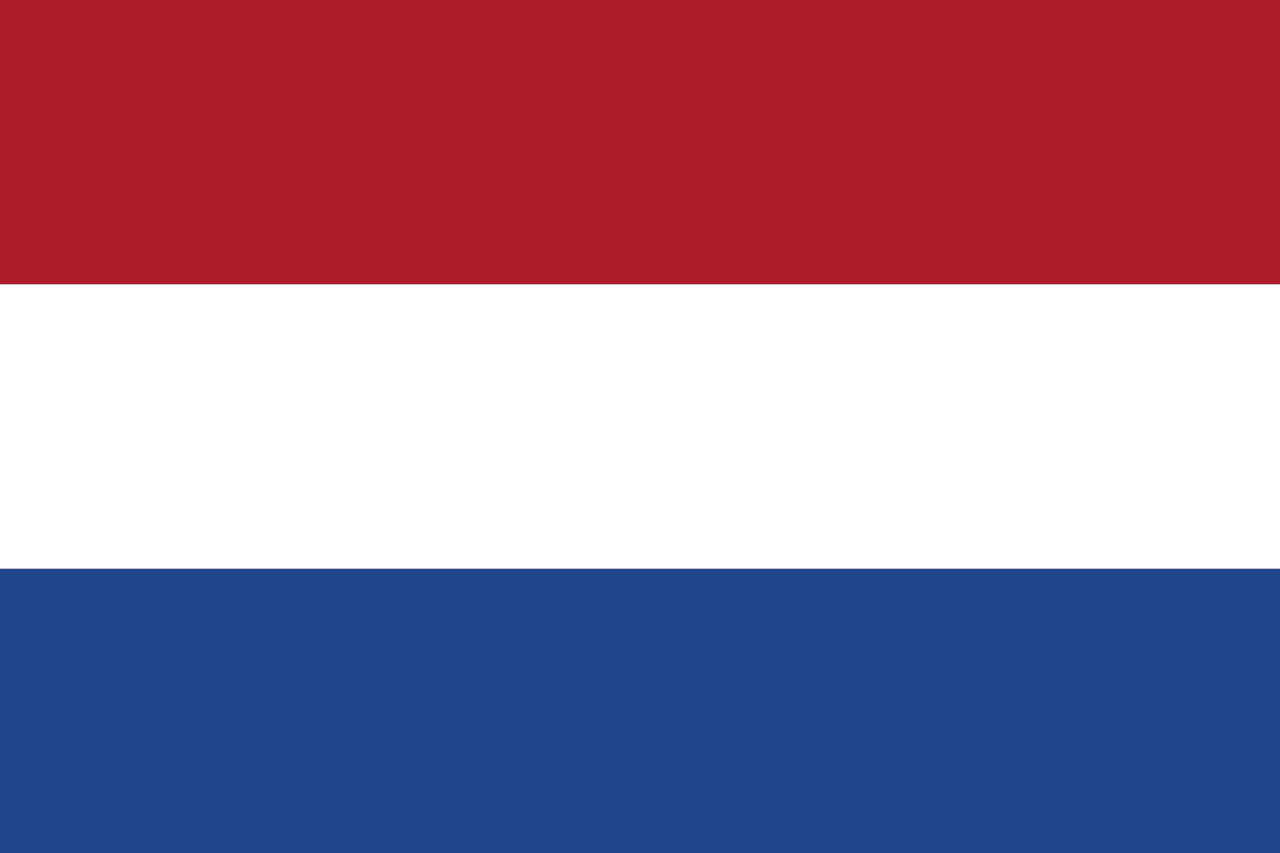

Netherlands
Europe
A horizontal tricolor of red, white, and blue, the oldest tricolor still in use today. It originated in the 16th century during the Dutch Revolt against Spain.
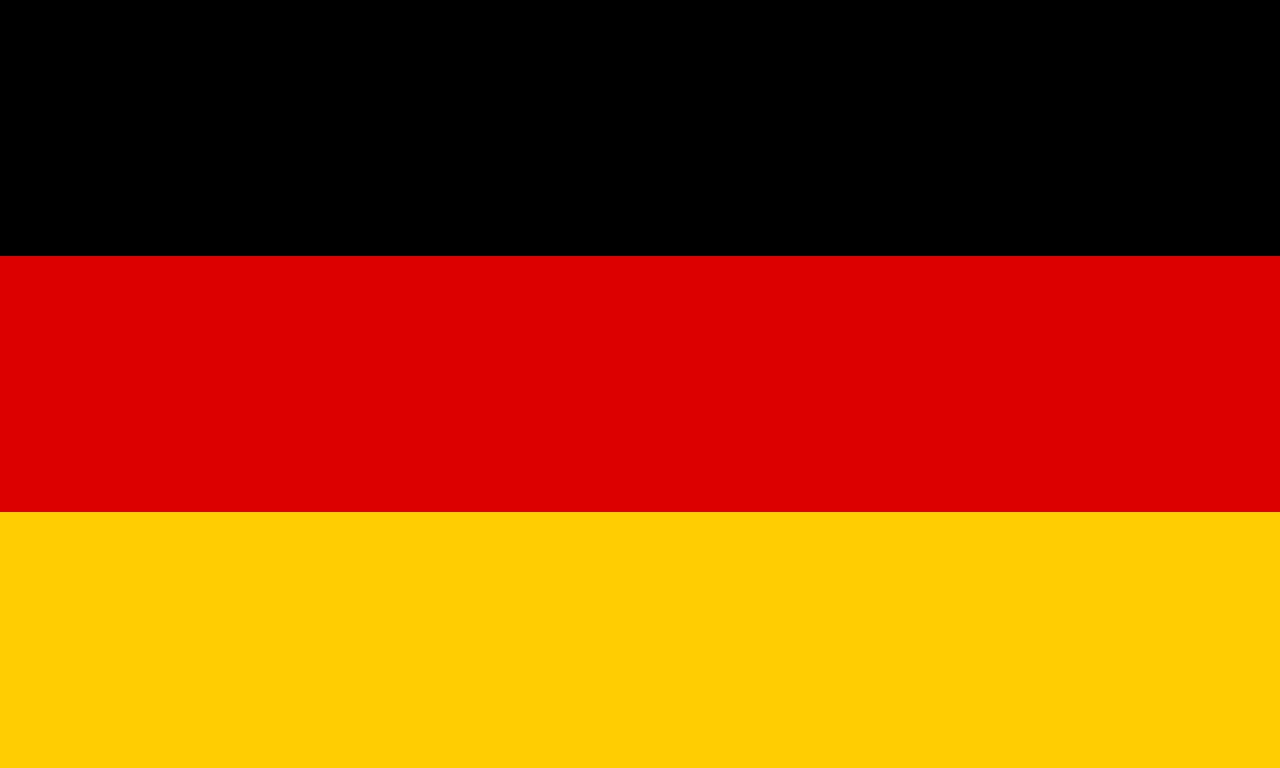

Germany
Europe
Three horizontal stripes of black, red, and gold representing the democratic traditions of Germany, with colors rooted in the 19th-century liberal movement and symbolizing unity, justice, and freedom in the modern Federal Republic.

Switzerland
Europe
A red square field with a white Greek cross in the center, representing the Christian faith that united the early Swiss cantons and the blood shed in defense of freedom, with origins dating back to the Holy Roman Empire and medieval Swiss military banners.
France
Europe
Revolutionary tricolor symbolizing liberty, equality, and fraternity.

Liechtenstein
Europe
Two horizontal stripes of blue and red with a golden crown in the upper left corner, representing this Alpine principality that is one of the world's smallest and wealthiest nations.