Bahamas Flag Meaning
Three horizontal stripes of aquamarine, gold, and aquamarine with a black equilateral triangle at the hoist, representing the waters surrounding the islands, the golden beaches and sunshine, and the strength and determination of the Bahamian people united in their love for their homeland.
- Continent
- North America
- Adopted
- 1973
- Ratio
- 1:2
- Colors
- aquamarine, yellow, black
- Designer
- Dr. Hervis Bain
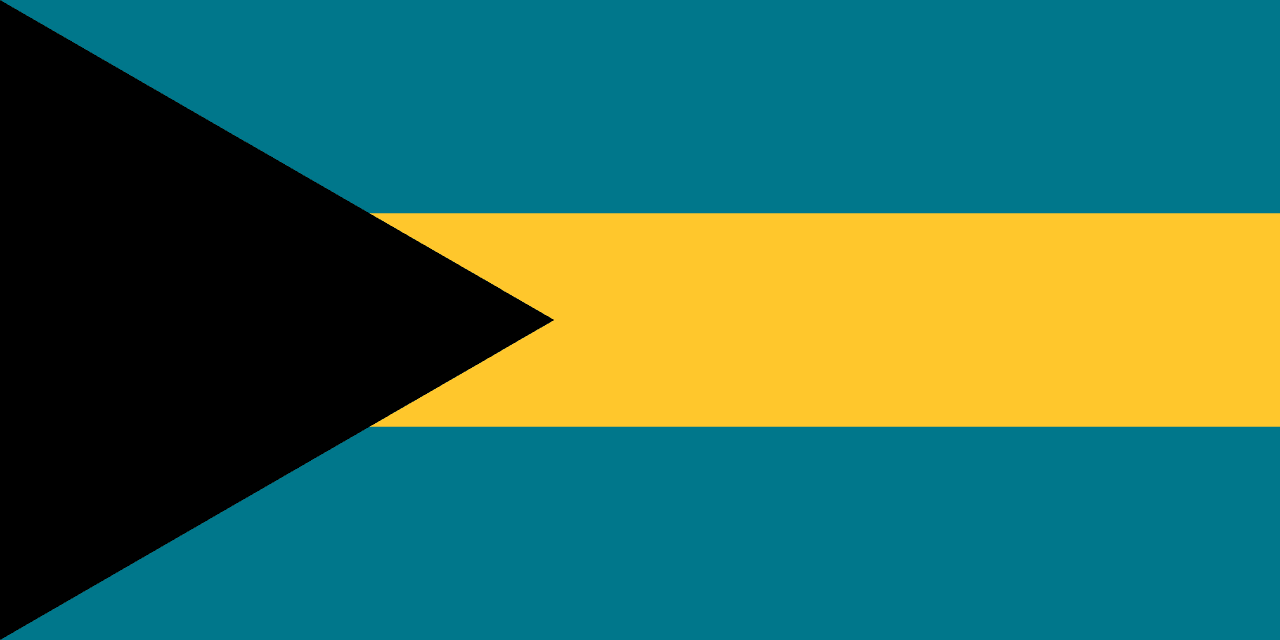
Symbolism
Aquamarine Stripes: Represent the crystal-clear turquoise waters of the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean that surround the 700 islands and cays of the Bahamas, symbolizing the marine environment that defines island life.
Gold Stripe: Represents the golden beaches and abundant sunshine that make the Bahamas a tropical paradise, as well as the bright economic future and natural resources of the island nation.
Black Triangle: Represents the strength, vigor, and determination of the Bahamian people to develop their rich natural resources, both on land and sea, while maintaining unity and progress as a nation.
Triangle Pointing Inland: The triangle points toward the country's natural resources and inland development potential, symbolizing the people's focus on building their nation's future rather than looking outward for solutions.
History
- Pre-1492: The Lucayan people, an Arawakan-speaking group related to the Taíno, inhabited the islands for over 1,000 years, developing a sophisticated maritime culture adapted to island life.
- October 12, 1492: Christopher Columbus made his first landfall in the New World on San Salvador Island in the Bahamas, beginning European contact that would devastate the indigenous population.
- 1513-1648: Spanish slave raids depopulated the islands of their indigenous inhabitants, leaving the Bahamas largely uninhabited until English colonists from Bermuda established settlements.
- 1670s-1720s: Pirates including Blackbeard used Nassau as a base for attacking Spanish treasure fleets, creating a 'Pirate Republic' until British naval forces restored order.
- 1783: American Loyalists fleeing the Revolutionary War brought enslaved Africans to establish cotton plantations, though the thin soil made large-scale agriculture unsuccessful.
- 1834: Slavery was abolished throughout the British Empire, leading to the development of a largely free black population that would eventually form the majority of Bahamian society.
- 1920-1933: Prohibition in the United States made the Bahamas a major center for rum-running, bringing prosperity and establishing the islands' reputation as a haven for questionable financial activities.
- 1940-1967: The development of tourism, particularly from the United States, transformed the Bahamian economy and led to demands for greater self-government and civil rights for the black majority.
- 1967: The Progressive Liberal Party under Lynden Pindling won elections, ending white minority rule and beginning the path to independence under black majority leadership.
- July 10, 1973: The Bahamas gained independence from Britain under Prime Minister Lynden Pindling, adopting the current flag design and becoming a sovereign nation within the Commonwealth.
- 1980s-1990s: Drug trafficking through the Bahamas to the United States created corruption scandals and security challenges, while offshore banking grew as an important economic sector.
- 2019: Hurricane Dorian, one of the most powerful storms ever recorded, devastated the northern islands, highlighting the vulnerability of small island states to climate change.
Trivia
- The Bahamas consists of about 700 islands and cays, but only about 30 are inhabited, with New Providence (home to Nassau) containing about 70% of the population.
- The flag represents a country that is only 50 miles from Florida, making it one of the closest Caribbean nations to the United States and heavily influenced by American culture and tourism.
- Nassau's Harbor is one of the world's busiest cruise ship ports, with over 5 million visitors annually making tourism the backbone of the Bahamian economy.
- The Bahamas is famous for its swimming pigs on Big Major Cay, where wild pigs swim out to boats for food, becoming one of the world's most unusual tourist attractions.
- Bahamian English (Bahamian Creole) is the everyday language, blending English with African linguistic influences, while Standard English is used in formal settings.
- The flag flies over a country where conch (pronounced 'konk') is the national symbol and main ingredient in traditional dishes like conch fritters and conch salad.
- The Bahamas has no income tax, capital gains tax, or inheritance tax, making it a popular destination for wealthy individuals and international businesses seeking tax advantages.
- The country is home to the world's deepest blue hole, Dean's Blue Hole on Long Island, which reaches a depth of 663 feet and attracts free divers from around the world.
- Junkanoo, the national festival celebrated around Christmas and New Year, features elaborate costumes, music, and dancing with roots in West African traditions.
- The flag represents a country where the majority of the population is of African descent, descendants of enslaved people and free blacks who settled in the islands.
- The Bahamas has more than 50 different shark species in its waters, making it one of the world's premier destinations for shark diving and marine research.
- Cable Beach in Nassau was named after the telegraph cable laid between the Bahamas and Florida in the 1890s, connecting the islands to international communication.
- The country has a stable democracy with regular elections, though the same two parties (PLP and FNM) have alternated power since independence.
- Traditional sloop sailing and regatta racing remain important cultural activities, with the National Family Island Regatta being a major annual celebration of maritime heritage.
- The flag represents a nation highly vulnerable to climate change, with most of its land area less than 5 feet above sea level and facing threats from rising seas and stronger hurricanes.
Related Countries
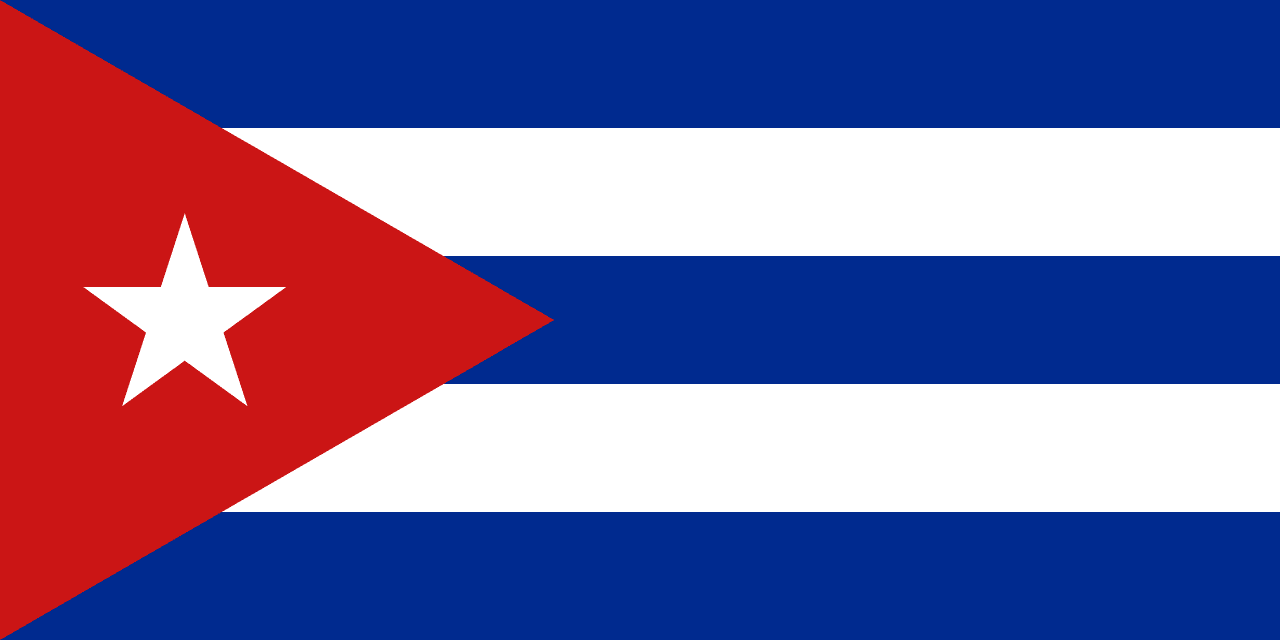

Cuba
North America
Five horizontal stripes alternating blue and white with a red equilateral triangle at the hoist containing a white five-pointed star, representing the three original provinces, purity, the blood of martyrs, and the independence of Cuba.

Jamaica
North America
A diagonal cross pattern dividing the flag into four triangles, with green triangles at top and bottom, black triangles at hoist and fly, and yellow diagonal cross, symbolizing the natural beauty, strength of the people, and golden sunshine of Jamaica.
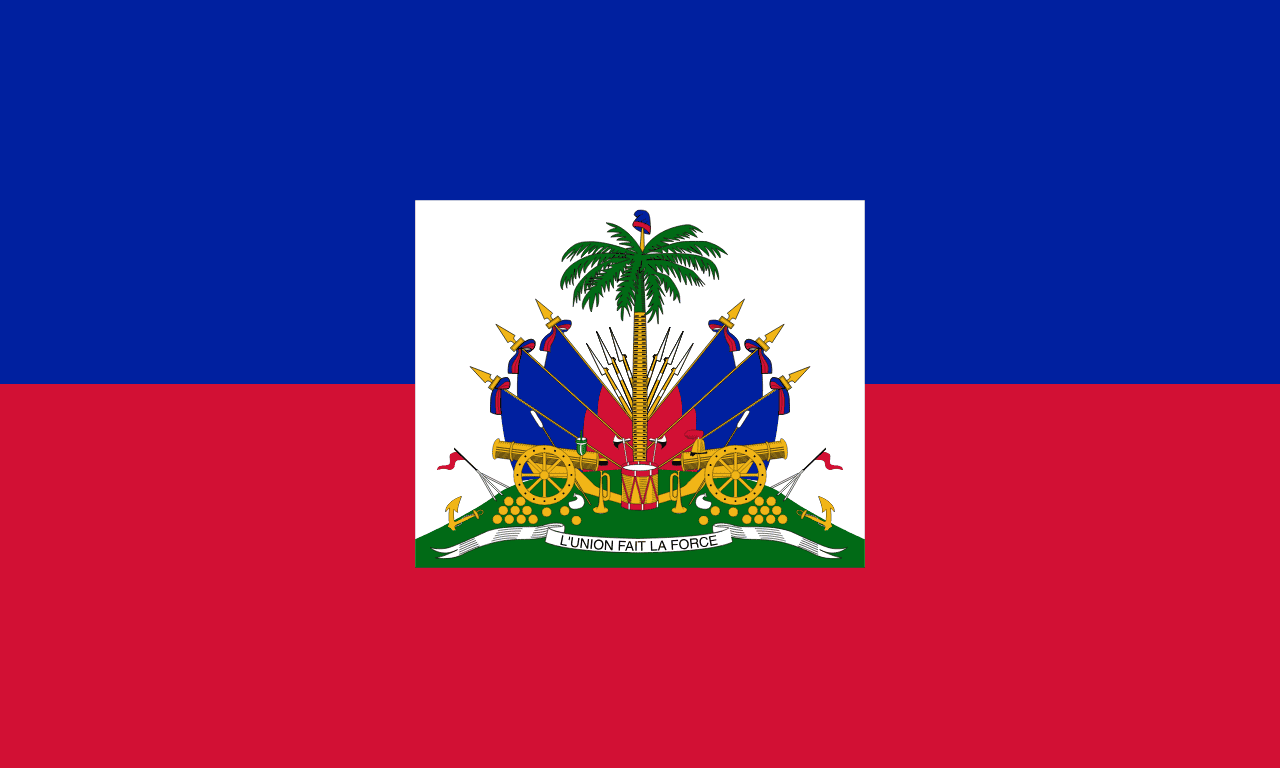
Haiti
North America
Two horizontal stripes of blue over red, representing the union of black and mixed-race Haitians and the blood shed for independence, making Haiti the first independent black republic and symbol of successful slave revolution.

Dominican Republic
North America
Four quarters alternating blue and red separated by a white cross, with the national coat of arms in the center, representing liberty, the blood of heroes, salvation and peace, and the Christian faith of the Dominican people.

Honduras
North America
Three horizontal stripes of blue, white, and blue with five blue five-pointed stars arranged in an X pattern on the white stripe, representing the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, peace, and the hope for Central American unity.

Belize
North America
A blue field with red stripes along the top and bottom edges and the national coat of arms in a white circle at the center, representing the ruling People's United Party, the opposition United Democratic Party, and the peace that unites them, making it the only national flag to feature human figures.