Åland Islands Flag Meaning
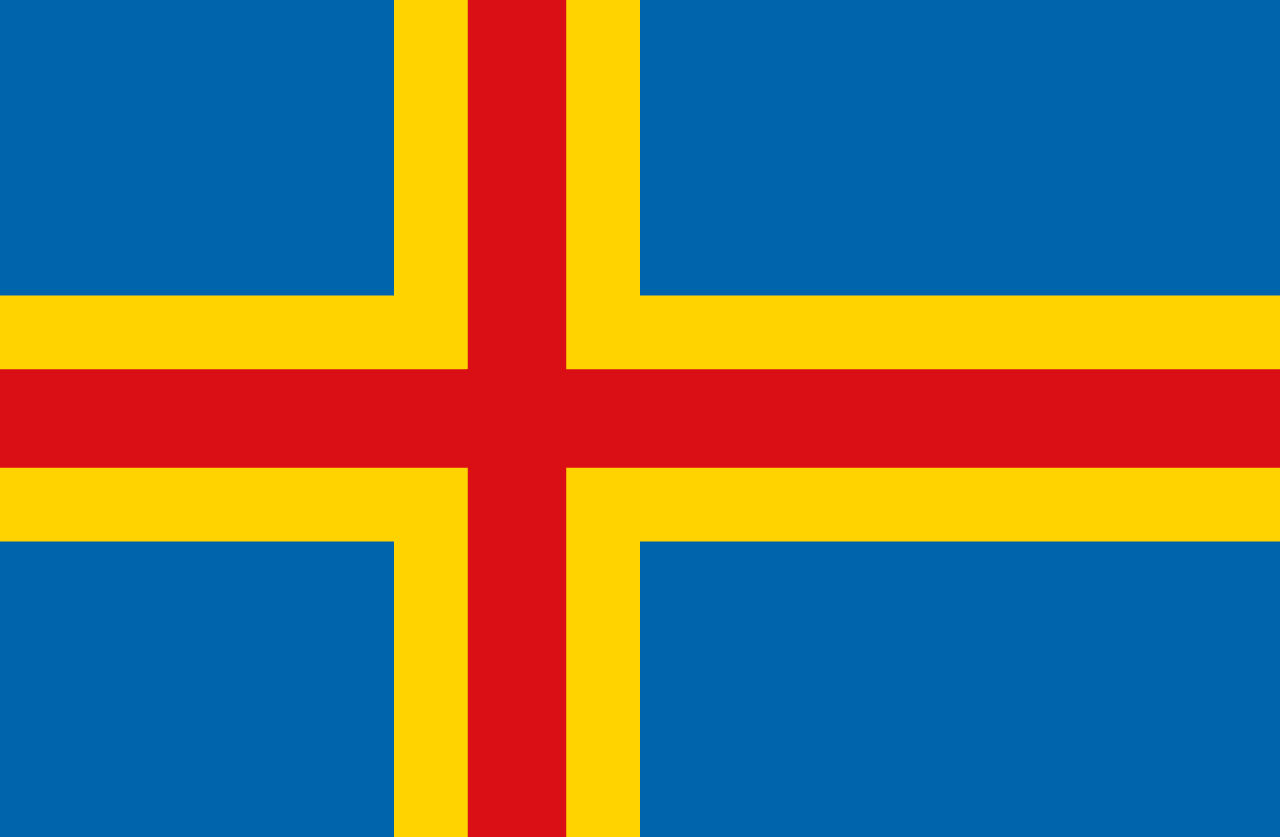
Tucked between Sweden and Finland, the Åland Islands possess a flag that tells the story of a small community balancing geography, culture, and politics. Adopted in 1954, the banner features a golden-bordered red cross set against a blue field, a striking fusion of Nordic tradition and local identity. Its design nods both to Finland, the sovereign state to which Åland belongs, and to Sweden, with which the islands share language and heritage. More than a decorative emblem, the flag is a quiet declaration of autonomy. It's a reminder that this archipelago, though small in population, carries a distinct voice within the Nordic world. To trace its colors and cross is to uncover a history of compromise, self-government, and the enduring importance of symbols in defining a people’s place.
- Continent
- Europe
- Adopted
- 1954
- Ratio
- 17:26
- Colors
- blue, yellow, red
Symbolism
Blue Field: Represents the Baltic Sea that surrounds the archipelago and connects the islands to both Finland and Sweden, emphasizing their maritime identity and geographic position.
Yellow Nordic Cross: Symbolizes the Swedish heritage, culture, and language of the Åland population, reflecting their historical connection to Sweden and Scandinavian identity.
Red Cross Within Yellow: Represents Finland and the islands' political connection to the Finnish state, acknowledging their status as an autonomous territory within Finland.
Nordic Cross Design: Connects Åland to the broader Scandinavian family of nations and emphasizes their Nordic cultural identity, despite being politically part of Finland.
Triple Cross Symbolism: The combination of blue field with yellow and red crosses uniquely represents the three-way cultural and political relationship between Åland, Sweden, and Finland.
History
- 12th-18th Century: The Åland Islands were part of Sweden, developing a Swedish-speaking culture and Lutheran religious tradition that persists today.
- 1809: Following the Finnish War, Åland became part of the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland under Russian rule, along with the rest of Finland.
- 1917-1921: After Finnish independence, the majority of Ålanders wanted to rejoin Sweden, leading to the 'Åland Crisis' and intervention by the League of Nations.
- June 24, 1921: The League of Nations awarded Åland to Finland but required guarantees of autonomy, neutrality, and protection of Swedish language and culture.
- 1922: The Autonomy Act established Åland's self-governance, making it one of the world's most successful examples of territorial autonomy within a state.
- April 3, 1954: The Åland flag was officially adopted by the autonomous government, creating a unique symbol that reflects the islands' distinct identity within Finland.
- 1995-Present: When Finland joined the EU, Åland received special status allowing them to maintain their tax-free status and continue their unique relationship with both Finland and Sweden.
Trivia
- Åland is one of the few autonomous territories in the world with its own flag that differs significantly from its parent country's flag design.
- The islands are completely demilitarized and neutral by international treaty, making them unique in the Baltic Sea region during both world wars and the Cold War.
- Swedish is the only official language in Åland, and knowledge of Swedish is required for voting rights, despite being part of bilingual Finland.
- The flag features the distinctive 17:26 ratio, which is unusual among Nordic cross flags and reflects Finnish rather than Swedish proportional traditions.
- Åland issues its own postage stamps and has its own internet domain (.ax), emphasizing their autonomous status within Finland.
- The islands' strategic location in the Baltic Sea made them important during both World Wars, despite their neutral and demilitarized status.
- Åland has its own parliament (Lagting) and government, with powers over local affairs while Finland handles foreign policy and defense matters.
- The flag appears on Åland's own euro coins, as the territory has special status within the eurozone allowing continued tax-free sales to travelers.
- Ferry traffic between Finland and Sweden makes the Åland flag highly visible to millions of Baltic Sea travelers annually.
- The design influenced other autonomous territory flags and demonstrates how flags can represent complex political and cultural relationships.
- Åland celebrates Flag Day on April 3rd, commemorating both the flag adoption and their autonomous status within Finland.
- The islands compete separately from Finland in some international competitions, including the Island Games, where their flag represents their distinct identity.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, Åland's autonomous health authority could make independent decisions, highlighting their self-governance even in health matters.
- The flag protocol requires it to be flown alongside the Finnish flag on official buildings, symbolizing the dual identity of the territory.
- Environmental protection is a major focus in Åland, and the flag often appears at international environmental conferences where they represent sustainable island development.
Related Countries

Poland
Europe
A simple bicolor of white over red, reflecting Poland’s heraldry and national identity. The design is among the simplest yet most recognizable European flags.

Albania
Europe
A red field with a black two-headed eagle, one of Europe's oldest heraldic symbols representing Albanian independence, strength, and the legacy of medieval hero Skanderbeg.

Slovakia
Europe
A horizontal tricolor of white, blue, and red with the Slovak coat of arms placed toward the hoist. The coat of arms features a double silver cross rising from three blue hills, symbolizing Christianity and Slovakia’s mountainous landscape.
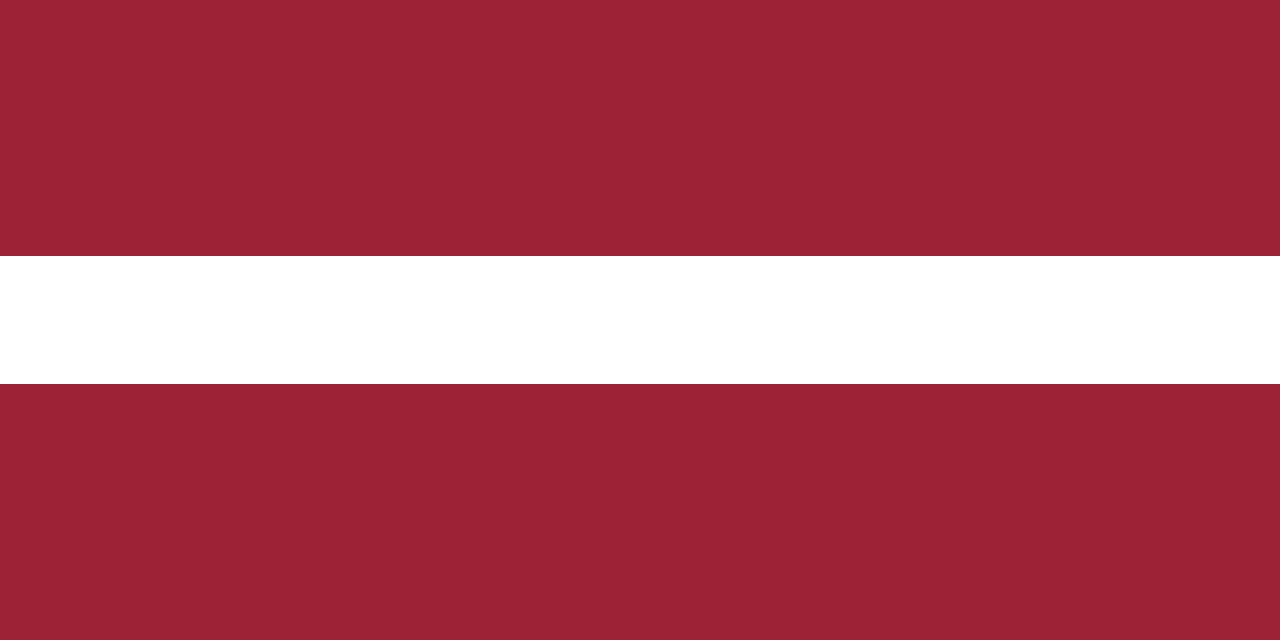

Latvia
Europe
Three horizontal stripes with dark red (maroon) stripes on top and bottom and a narrow white stripe in the center, representing one of the world's oldest flag designs dating back to medieval times and Latvia's struggle for independence.

Andorra
Europe
Three vertical stripes of blue, yellow, and red with the coat of arms centered on the yellow stripe, representing France and Spain (the co-princes), the principality itself, and the unique dual sovereignty arrangement that has governed this small Pyrenean state for over 700 years.
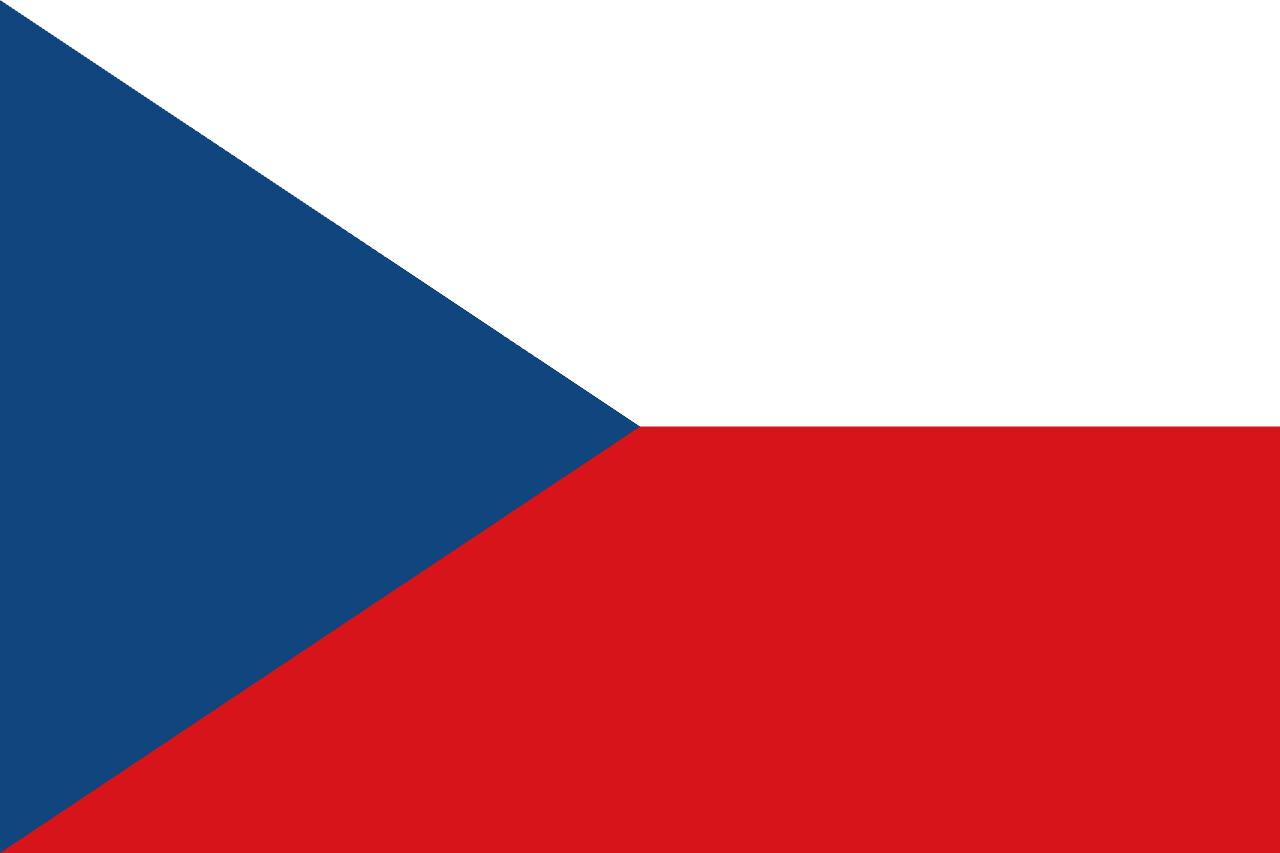
Czech Republic
Europe
Two horizontal stripes of white over red with a blue triangle extending from the hoist, combining Bohemian colors with Moravian blue, representing the historical lands and democratic ideals of the Czech nation.